Figure 4.
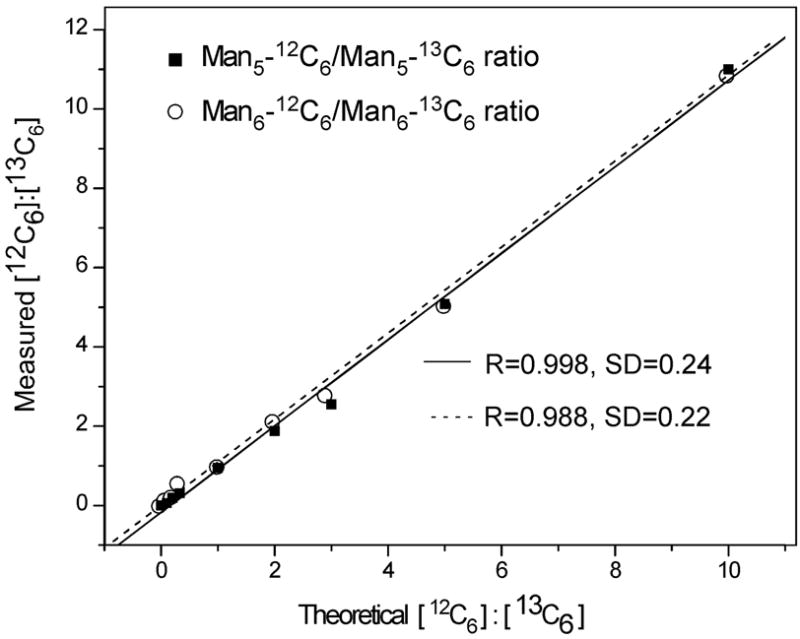
a: GRIL of glycans released by PNGase F from RNaseB. A mixture of free high mannose-type N-glycans Man5, Man6, Man7, Man8, and Man9 released by PNGase F digestion of RNaseB were labeled in separate reactions with [12C6]aniline or [13C6]aniline, mixed in exactly a 1:1 ratio and subjected to MALDI-TOF analysis. The masses of the individual glycans are shown associated with the most plausible structures represented with the symbols as shown in Fig. 1. For doublets found in the equimolar mixtures, the masses are shown below the structure and the ratio of the peak areas of glycan-[12C6]aniline: glycan-[13C6]aniline is shown (R). The inset represents an expansion of a portion of the spectrum. b: Use of GRIL to estimate relative amounts of glycan structures in glycan mixtures. N-glycans derived from RNase B were divided and separately derivatized with [12C6]aniline or [13C6]aniline and these were mixed in molar ratios of 10:1, 5:1, 3:1, 2:1, 1:1, 1:2, 1:3, 1:5, and 1:10 (based on absorption at 260 nm) and subjected to MALDI-TOF analysis. The linear relationship between expected ratios of heavy and light isotope included in the 8 mixtures and ratios calculated from the observed MALDI-TOF profiles of the Man5GlcNAc2-[12C6]aniline and -[13C6]aniline derivatives (■) and the Man6GlcNAc2-[12C6]aniline and -[13C6]aniline derivatives (○) are shown.

