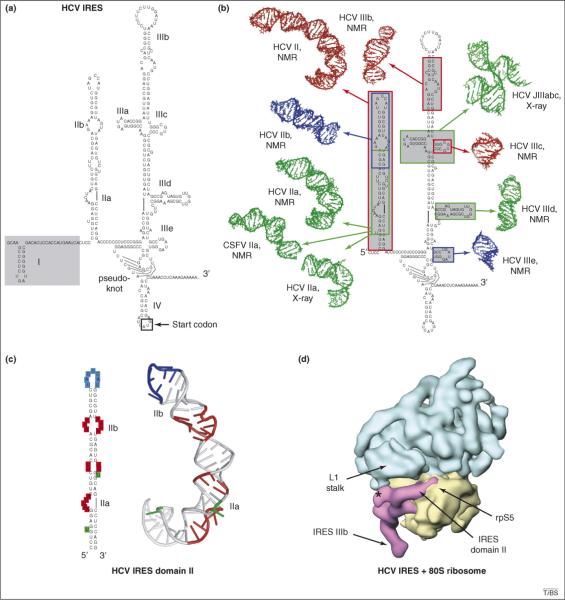
Figure 3.
Structures of the hepatitis C virus (HCV) IRES RNA. (a) Proposed secondary structure of the HCV IRES, with its stem-loops labeled. Stem-loop I and the portion of the RNA that is shaded can be removed without affecting IRES function. The extended stem-loop structure that contains internal loops IIa and IIb is generally referred to as ‘domain II’. In the HCV IRES, the AUG start codon is located in a stem-loop structure (IV), however, this stem-loop is not found in all related IRESs (such as that of CSFV). (b) At the left is the secondary structure of the HCV IRES surrounded by structures of secondary-structure elements solved by NMR and X-ray crystallography [40–47]. The location of each element in the structure is shown with arrows and boxes that correspond to the color of the structure. (c) Secondary structure of domain II of the HCV IRES and its 3D structure as solved by NMR [41]. Blue denotes the apical loop that is placed into the 40S subunit's E-site, red denotes internal loops IIa and IIb and green denotes bulged bases. These features cause the RNA to adopt an overall bent conformation. (d) HCV IRES RNA bound to a human 80S ribosome, with the IRES density in magenta, the 60S subunit in cyan and the 40S subunit in yellow. The location of the L1 stalk and rpS5 are indicated [50]. The asterisk denotes a putative interaction between domain I (which is not needed for IRES function) of the HCV IRES and the base of the L1 stalk.