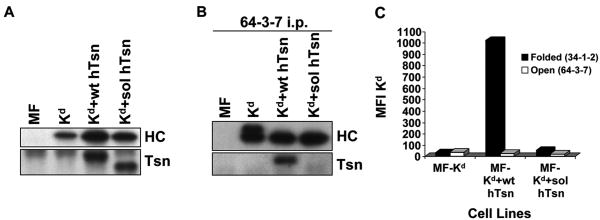
Figure 3.
(A) Tapasin and Kd were expressed at similar levels in Kd+wt hTsn relative to Kd+sol hTsn. Samples of lysates from MF, MF+Kd, MF+Kd+wt hTsn, and MF+Kd+sol hTsn were electrophoresed on a 10% acrylamide Tris-glycine gel for tapasin (Tsn) or on a 4→20% acrylamide Tris-glycine gel for Kd, the proteins were transferred to a blotting membrane and probed with Ab specific for human tapasin (Tsn) or with 64-3-7 to identify the total epitope-tagged Kd heavy chain (HC). (B) Soluble human tapasin binds very weakly to Kd. Open Kd heavy chains were immunoprecipitated from a digitonin lysate of each of the indicated cell types with the 64-3-7 mAb in the presence of 200 μM DSP. The immunoprecipitates were electrophoresed on acrylamide Tris-glycine gels, transferred to membranes, and probed with 64-3-7 to identify the immunoprecipitated open Kd heavy chain (HC) or with anti-tapasin mAb (Tsn) to identify the co-immunoprecipitated tapasin. (C) Soluble human tapasin did not enable Kd to be expressed at the surface of mouse cells. Cells were incubated with secondary antibody only, or an antibody against the folded form of Kd (34-1-2), or an antibody against the open form of Kd (64-3-7). Results obtained with the secondary antibody only were all less than 5.0. Values on the y axis are relative mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) units. Wt hTsn = wild type human tapasin; Sol hTsn = soluble human tapasin. Very similar results were obtained in a separate flow cytometry experiment.