Figure 3.
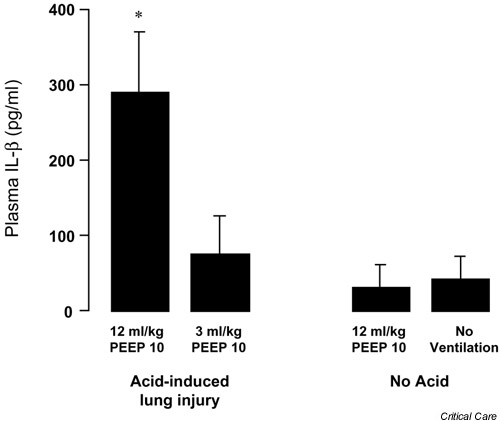
Plasma IL-1β following 4 hours of mechanical ventilation in a rat model of acid aspiration. Ventilation with a tidal volume of 12 ml/kg significantly increased plasma levels of IL-1β compared with rats ventilated with 3 ml/kg and a similar level of positive end expiratory pressure (PEEP; cmH2O) (*P < 0.05 by paired t test, mean ± standard deviation). IL-1β levels in the 3 ml/kg acid-injured group were not different from those in uninjured rats ventilated with 12 ml/kg or from uninjured, never ventilated rats (n = 5 in each acid injured group and n = 3 in the uninjured groups).
