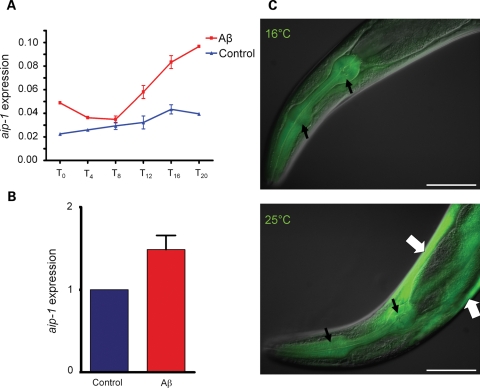
Figure 1.
Expression of the human amyloid-β42 leads to an increase in aip-1 transcript accumulation. (A) Induction of aip-1 shown using GeneChip microarrays (Affymetrix, Inc.). aip-1 levels in an Aβ-expressing strain, CL4176, were compared to a control strain expressing GFP. In these strains, Aβ42 or GFP were expressed at low levels at 16°C, while moving the animals to 25°C induced high levels of transgene expression (see Materials and Methods for details of temperature inducibility). Worms were harvested at the time of temperature change (T0) and every 4 h afterwards until 20 h later (T4–T20). Error bars represent the SEM. (B) Microarray data were confirmed using real-time RT–PCR to measure aip-1 levels at the T16 time point. Data were plotted as a fold change compared with the GFP control strain. Error bars represent the SEM. (C) Aβ and aip-1 expression were correlated in an aip-1/GFP transcriptional reporter strain. GFP fluorescence was detected in the pharynx at 16 and at 25°C (narrow black arrows), which is consistent with constitutive pharyngeal expression. In body wall muscle, however, GFP fluorescence was only detectable at 25°C (wide white arrows), which is consistent with Aβ42-stimulated induction of aip-1 promoter. Size bar = 100 µm.