Figure 6.
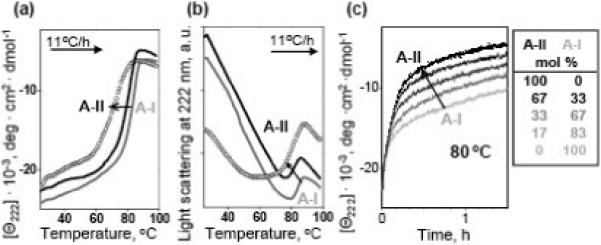
Effects of apoA-II on thermal stability of discoidal rHDL. Sample conditions are 20 μg/ mL protein in buffer A. DMPC complexes containing apoA-I alone (grey line), apoA-II alone (circle), or both apoA-I and apoA-II (black line) were heated at a rate of 11 °C/h, and the melting data were recorded at 222 nm by CD (a) and 90° light scattering (b). Black lines correspond to AII:A-I molar ratio of 1:2; the data at other ratios (not shown to avoid overlap) demonstrated a similar trend. (c) Time course of rHDL protein unfolding monitored by CD in a T-jump from 25−80 °C; arrow indicates increase in the apoA-II:apoA-I ratio (molar fractions are listed in the table). Increase in apoA-II:apoA-I ratio reduces the apparent melting temperature (a, b) and accelerates the denaturation of rHDL (c), indicating reduced stability.
