Figure 1.
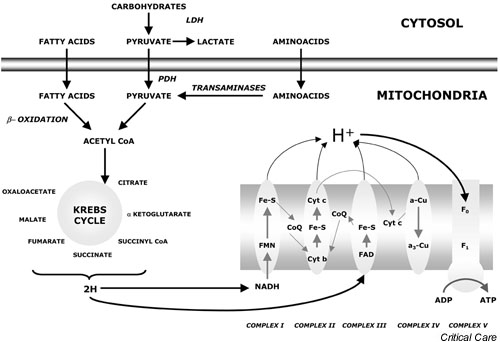
Mitochondrial electron chain transport and oxydative phosphorylation. Most of the energy produced by metabolic pathways is contained in the reduced form of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH) and in the reduced form of flavine adenine dinucleotide (FADH2), and is transformed in ATP by mitochondria. Reduced mitochondrial coenzymes give their two electrons to carriers that carry them to molecular oxygen, the final electron acceptor, using oxydo-reduction reactions. A protonic gradient allows hydrogen to cross the inner membrane and produce ATP. a-Cu, coenzyme a-copper; a3-Cu, coenzyme 13-copper; CoA, coenzyme A; CoQ, coenzyme Q; Cyt, cytochrome; F0, F0 family ATP synthase; F1, F1 family ATP synthase; Fe-S, iron-suphur cluster; FMN, flavine-adenine mononucleotide; H, hydrogen; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; PDH, pyruvate dehydrogenase.
