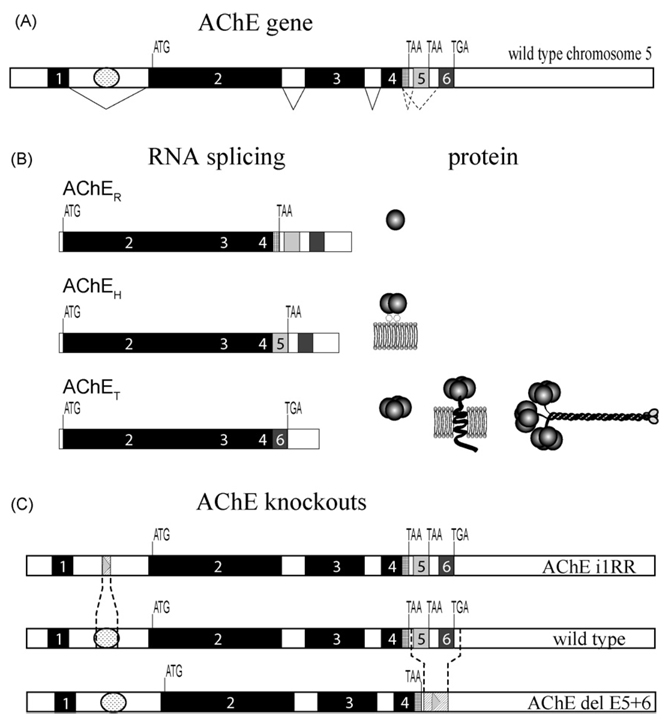
Fig. 1.
(A) AChE gene structure showing invariantly spliced exons 1–4 and alternatively spliced exons 5 and 6. ATG denotes translational start signal, TGA and TAA are translational stops. Invariant splicing is shown by solid lines while alternative splicing is indicated by dotted lines. The regulatory region in the first intron is depicted by a oval between exons 1 and 2. (B) Three AChE variants AChER, AChEH and AChET RNAs are produced by alternative splicing and generate a diversity of AChE molecular forms. (C) Map of the AChE gene with the wild-type and knockout mouse strains with the regions of deletion shown.