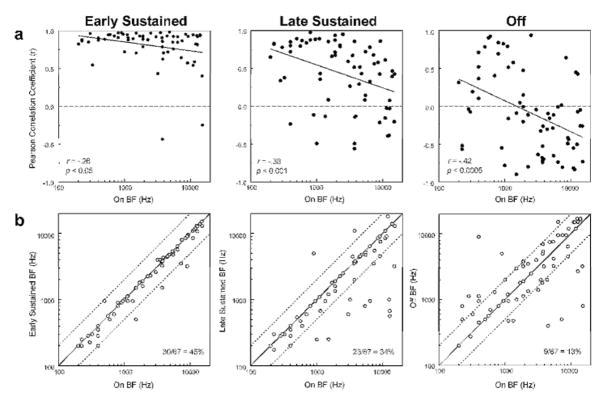
Figure 4.
a, Pearson correlation coefficients quantifying the relationship between the FRF for the time window indicated at the top of each column and the corresponding FRF for the “on” time window plotted as a function of “on” BF. Correlation coefficients tend to decrease with increasing “on” BF (as represented by the significant negative Pearson correlation coefficients and negatively sloped regression lines shown in the plots). Correlation coefficients become increasingly negative for later time windows, indicating a greater prevalence of inversely tuned “on” and later responses. b, BF of “early sustained”, “late sustained”, and “off” responses are plotted against BF of “on” responses to illustrate changes in BF over the course of the response. Data points falling on the diagonal represent identical BFs for “on” and later responses. Values one octave above and below the “on” BF are represented by the dashed lines. Proportion of sites displaying identical BFs for the “on” time window and for the specified later time window is indicated in the plots. Deviations in BF tend to become more prevalent for later time windows.