Fig. 6.
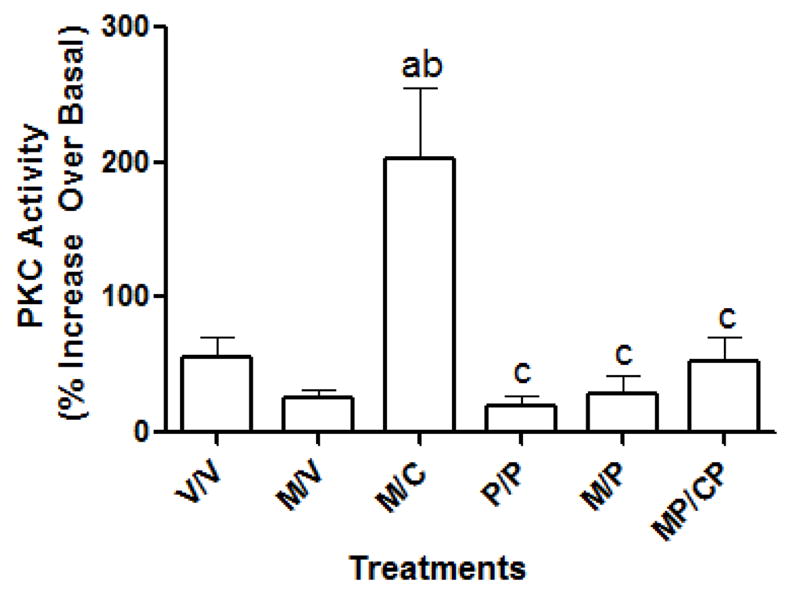
The effect of pertussis toxin on the enhancement of PKC induced following microtubule depolymerization. As shown, Colcemid, added during the 16 hr withdrawal period following either a vehicle pretreatment (V/C) or a melatonin pretreatment (M/C), enhanced PKC activity following a 10nM melatonin re-challenge when compared to vehicle-treated cells (V/V) or melatonin-treated cells (M/V), respectively. However, when pertussis toxin was added along with Colcemid during the 16 hr withdrawal period (MP/CP), this enhancement of PKC activity by 10 nM melatonin was blocked. The addition of pertussis toxin either after melatonin pretreatment (M/P) or alone (P/P) was without effect. All data were analyzed by 1-way ANOVA followed by a Newman-Keuls Post-hoc t-test where (a)= P<0.05 when compared to V/V; (b)=P<0.05 when compared to M/V; (c) =P<0.05 when compared to M/C.
