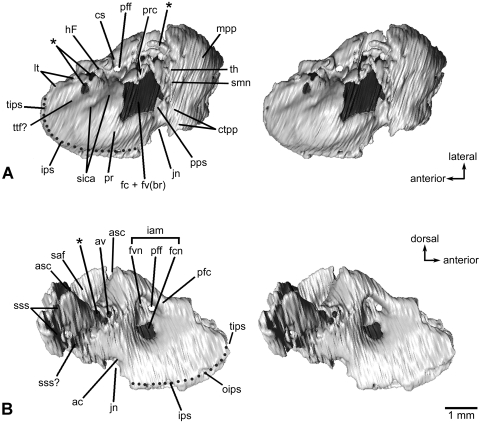
Fig. 3.
Left petrosal bone of Henkelotherium guimarotae(Gui Mam 138/76b). Virtual reconstruction from computed tomography scans. (A) Ventral (tympanic) view (stereo pair); (B) dorsomedial (endocranial) view (stereo pair). Dark grey pattern indicates the exposed inner ear bony labyrinth (including damaged area). Asterisks are opening(s) caused by damage and are not the original anatomical structures. Dotted line refers to the canal of the inferior petrosal sinus. ac, opening of aqueductus cochleae; asc, anterior semicircular canal (broken); av, opening of aqueductus vestibuli; cs, cavum supracochleare (housing the geniculate ganglion of the facial nerve, broken and incomplete); ctpp, caudal tympanic process of petrosal; fc + fv(br), broken areas of the fenestra cochleae and fenestra vestibuli (possibly including the fossa for the stapedius muscle); fcn, foramen for cochlear nerve (cranial nerve VIII); fvn, foramen for vestibular nerve; hF, hiatus Fallopii (opening for the greater superficial petrosal nerve of the facial nerve, broken and open); iam, internal acoustic meatus; ips, canal for inferior petrosal sinus; jn, jugular notch (incomplete); lt, lateral trough (incomplete); mpp, mastoid part of petrosal (mastoid exposure of the pars canalicularis); oips, opening for inferior petrosal sinus, pfc, prefacial commissure; pff, primary foramen for facial nerve (cranial nerve VII); pps, post-promontorial tympanic sinus; pr, promontorium; prc, prootic canal (broken and open); saf, subarcuate fossa (incomplete); sica, sulcus for internal carotid artery; smn, stylomastoid notch (exit for facial nerve); sss, sulcus for sigmoid sinus; sss?, possible sulcus for sigmoid sinus; th, attachment for tympanohyal; tips, tributary of inferior petrosal sinus; ttf?, possible tensor tympani fossa.