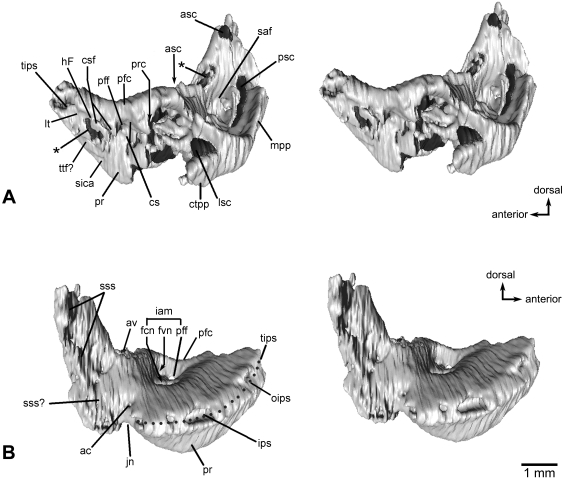
Fig. 4.
Left petrosal bone of Henkelotherium guimarotae(Gui Mam 138/76b). Virtual reconstruction based on computed tomography scans. (A) Lateral view (stereo pair); (B) medial view (stereo pair). The vestibular portion and lateral trough area are damaged and the rostrodorsal part is missing. Asterisks indicate openings caused by damage. ac, opening of aqueductus cochleae; asc, anterior semicircular canal (broken and open); av, opening of aqueductus vestibuli; cs, cavum supracochleare; csf, cavum supracochleare floor (remnant of the broken and incomplete cavum); ctpp, caudal tympanic process of petrosal; fcn, foramen for cochlear nerve; fvn, foramen for vestibular nerve; hF, hiatus Fallopii (opening for the greater superficial petrosal nerve of the facial nerve, open and broken); iam, internal acoustic meatus; ips, canal for inferior petrosal sinus; jn, jugular notch (incomplete); lsc, lateral semicircular canal (broken and incomplete); lt, lateral trough (broken); mpp, mastoid part of petrosal (mastoid exposure of the pars canalicularis); oips, opening of inferior petrosal sinus; pfc, prefacial commissure; pff, primary facial foramen; pr, promontorium; prc, prootic canal (broken and open); psc, posterior semicircular canal (broken and open); saf, subarcuate fossa (broken and incomplete); sica, sulcus for internal carotid artery; sss, sulcus for sigmoid sinus; tips, tributary of inferior petrosal sinus; sss?, possible sulcus for sigmoid sinus; ttf?, possible tensor tympani fossa.