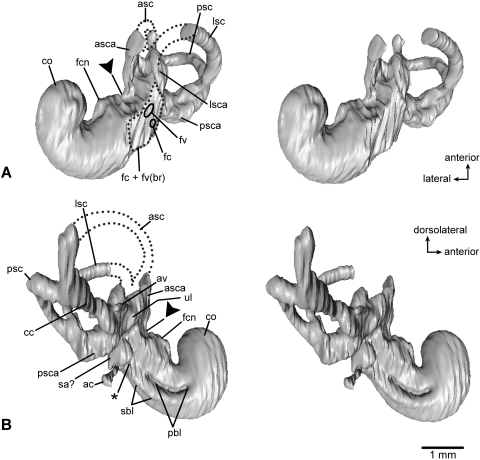
Fig. 6.
Virtual endocast of the inner ear bony labyrinth of Henkelotherium guimarotae type specimen (Gui Mam 138/76b), left side. Asterisk indicates the separation between the saccular space and the base of cochlear canal. Dark triangles indicate the separation between the utricle and saccule. (A) Ventrolateral view (stereo pair); (B) dorsomedial view (stereo pair). ac, aqueductus cochleae (endocast); asc, anterior semicircular canal (incomplete, broken segment indicated by dotted lines); asca, anterior semicircular canal ampulla; av, aqueductus vestibuli (endocast); cc, crus commune; co, cochlear duct (endocast); fc + fv(br), dashed outline indicating the broken area of fenestra cochleae, fenestra vestibuli and possibly the fossa for the stapedius muscle; fc, hypothetical position of fenestra cochleae (not preserved); fcn, foramen for cochlear nerve; fv, hypothetical position of fenestra vestibuli (not preserved); lsc, lateral semicircular canal (incomplete, broken segment indicated by dotted lines); lsca, lateral semicircular canal ampulla; pbl, primary bony lamina for basilar membrane; psc, posterior semicircular canal; psca, posterior semicircular canal ampulla; sa?, possible saccular part of vestibule; sbl, secondary bony lamina for basilar membrane; ul, utricle.