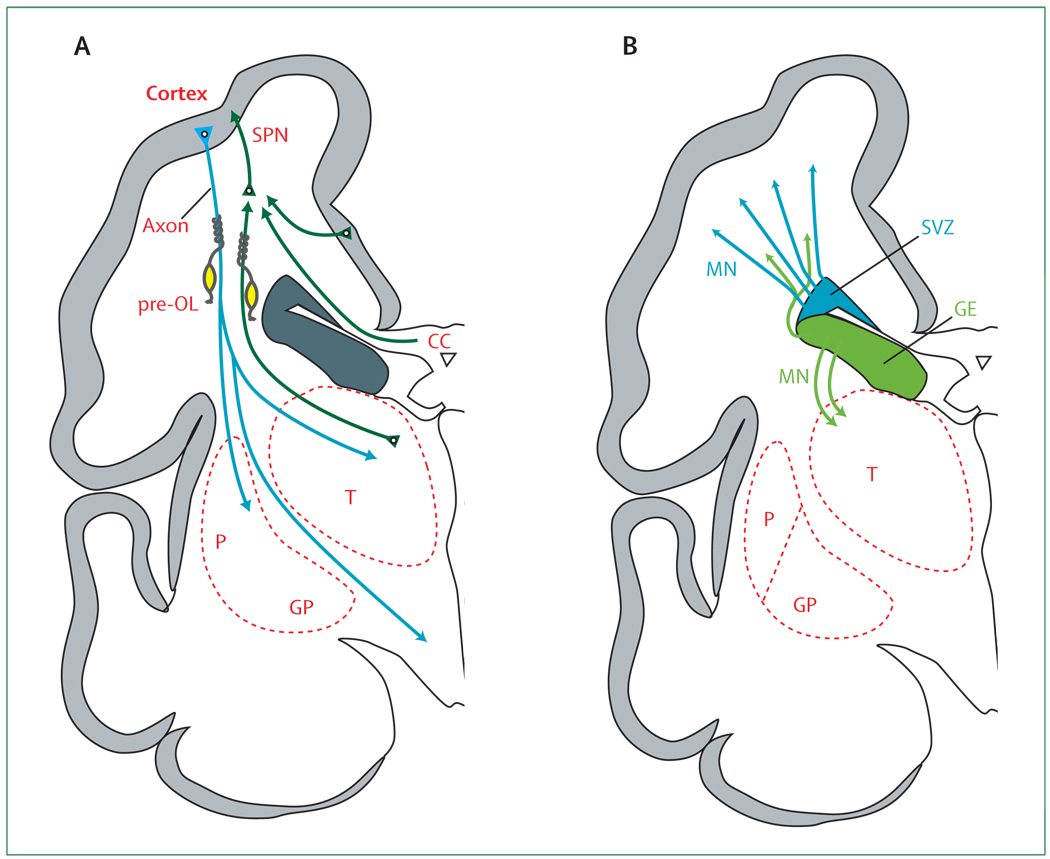
Figure 3. Cerebrum in coronal section at 28 weeks’ gestation showing critical events in cortical development.
(A) The axons (green) emanate from the thalamus (T; projection fibres), corpus callosum (CC; commissural fibres), and cortex (association fibres), which synapse initially on subplate neurons (SPNs). SPNs send axons to the cortex and promote cortical development before the thalamo-cortical and cortico-cortical fibres enter the cortex. From the cortex, axons (blue) descend to the thalamus, basal ganglia, and corticospinal (and corticopontine) tracts. Premyelinating oligodendrocytes (pre-OLs; yellow) enstheath axons before full differentiation to mature myelin-producing oligodendrocytes. (B) The proliferation and migration of GABAergic interneurons from the subventricular zone (SVZ) and ventral germinative epithelium of the ganglionic eminence (GE) are shown. Neurons from the SVZ (blue) migrate radially to the cortex and from the GE (green), tangentially and then radially, to the cortex. The migrating stream of interneurons from the GE to the dorsal thalamus is also shown. GP=globus pallidus. MN=migrating neurons. P=putamen.