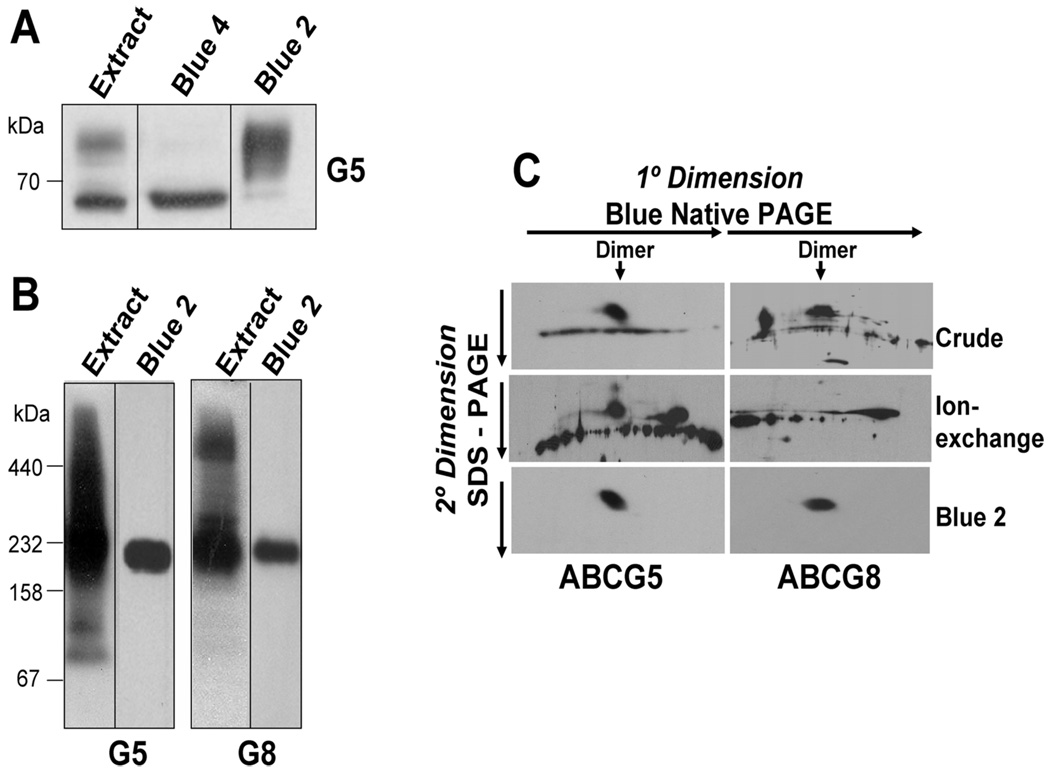
FIGURE 2.
Solubilization of native G5G8 and separation of mature G5G8 from the immature forms of the half-transporters. Postnuclear liver membranes from wild-type mice were prepared and solubilized as described in the Experimental Procedures. (A) Immature (ER) and mature forms of G5 and G8 were separated by sequential Blue 4 and Blue 2 chromatography, as described in the Experimental Procedures. The crude detergent extract (25 µg), the proteins eluted from the Blue 4 column by 1.5 M NaCl and further purified by glycerol-gradient centrifugation (10 µg), and the Blue 2 column eluate (2 µg) were subjected with SDS–PAGE and immunoblotted with an anti-G5 Ab. (B) Oligomeric structure of G5 and G8 in the crude detergent extract and the Blue 2 column fraction from wild-type mouse livers. Crude detergent extract of wild-type mouse liver membranes (60 µg) and the Blue 2 column eluate (5 µg) were resolved by BN–PAGE and analyzed by immunoblotting using antibodies to G5 and G8. (C) Lanes from the gel shown in B containing the crude membrane extract and the eluate from the Blue 2 column were cut into strips and placed horizontally on a SDS–PAGE gel (10%). Also included in the experiment was an ion-exchange column (Mono Q) fraction of the crude extract. The SDS–PAGE was run as the second dimension and analyzed by Western blotting using anti-G5 and anti-G8 antibodies.