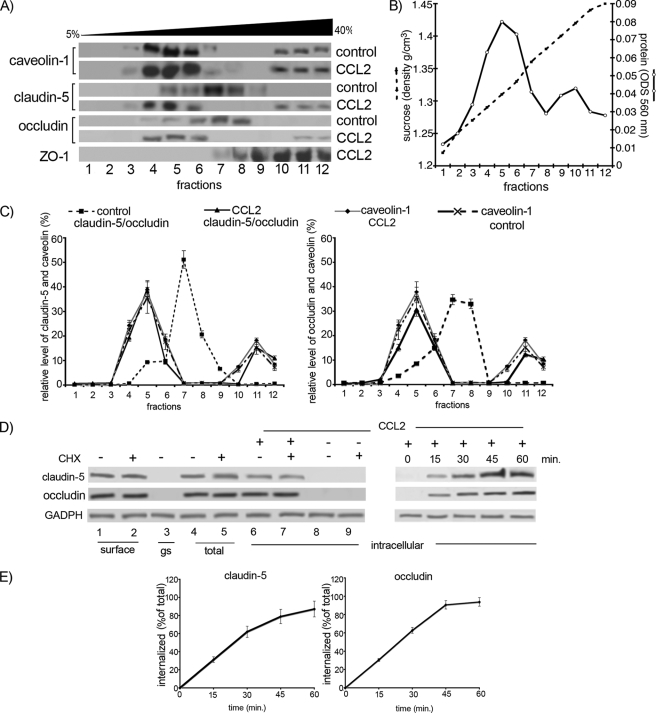
FIGURE 4.
A, mBMEC monolayers were treated with CCL2 for 30 min at 37 °C, and Triton X-100-soluble and Triton X-100-insoluble fractions were prepared. The Triton X-100-insoluble fraction was layered on a 5–40% sucrose gradient, and 12 fractions were separated (1–12). All fractions were analyzed by Western blotting using an anti-caveolin-1, -claudin-5, and -occludin antibodies. The caveolin-containing fractions (4–6 and 10–12) also contained claudin-5 and occludin in CCL2-treated mBMEC. B, each collected fraction (1 ml of total volume) was first analyzed for protein concentration (○) and sucrose density (●) using a refractometer before Western blot analysis was performed. This graph represents at least five independent experiments. C, relative levels of occludin and claudin-5 in individual fractions from control cells or cells treated with CCL2 for 30 min. The collected fractions were subjected to Western blot analysis, obtained data were scanned, and bands were analyzed by densitometry using ImageJ software. The graphs represent at least five independent experiments. Under control conditions a large portion of claudin-5 and occludin is in fractions 7 and 8, fractions without caveolin 1. However, after CCL2 treatment, claudin-5 and occludin are found in fractions 4, 5, 6, 11, and 12. These fractions are those containing caveolin-1. CCL2 had no apparent effect on the distribution of caveolin-1 between different fractions. D, internalization of surface biotinylated claudin-5 and occludin proteins. Confluent mBMECs, treated with and without cycloheximide (CHX), were surface-biotinylated at 0 °C and then exposed to CCL2 for 30 min at 37 °C to allow internalization. Any membrane-bound biotin was removed by glutathione solution (glutathione stripping, gs). Lanes 1 and 2, biotinylated claudin-5 and occludin at the cell surface; lane 3, glutathione stripping of surface biotin; lanes 4 and 5, total cell lysate; lanes 6–9, portion of biotinylated internalized proteins. Adjusted blot showing the time course (0–60 min) of internalized biotinylated claudin-5 and occludin during mBMEC exposure to CCL2. E, quantification of internalized occludin and claudin-5 during the exposure to CCL2 and opening of brain endothelial barrier. The percentage of internalized protein was estimated as the percentage of total biotinylated occludin and claudin-5. GADPH represents an internal loading control. Data represent average ± S.D. of five independent experiments.