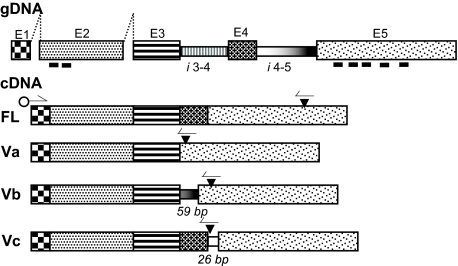
FIGURE 1.
HAS1-FL and HAS1-Vs constructs. This drawing illustrates the cDNA constructs of HAS1-FL and all the variants (HAS1-Va, HAS1-Vb, and HAS1-Vc) with genomic sequence (gDNA) (top bar) (5). E1–E5 are exons, and i3-4 and i4-5 are the introns joining E3 to E4 and E4 to E5, respectively. Thick black bars under E2 and E5 show positions coding transmembrane domains (not scaled). Filled triangles on cDNAs point to stop codons, half-arrows indicate PCR primer positions for reverse transcription-PCR, and open circles indicate the position of 10 amino acid tags when subcloned in the expression vector. HAS1-Va results from skipping of E4, which leads to formation of a frameshift generated a premature termination codon (fg-PTC) at 56 bp downstream of the deletion. HAS1-Vb results from skipping of E4 and partial retention of the last 59 bp of the 3′ part of i4-5 joining to the 5′-end of E5 and thus formation of an fg-PTC at 93 bp downstream of E5. HAS1-Vc results from retention of first 26 bp of the 5′ part of i4-5 joining to the 5′-end of E5 without any exon skipping and thus formation of an fg-PTC 1 bp downstream of the retained 26-bp partial intron.