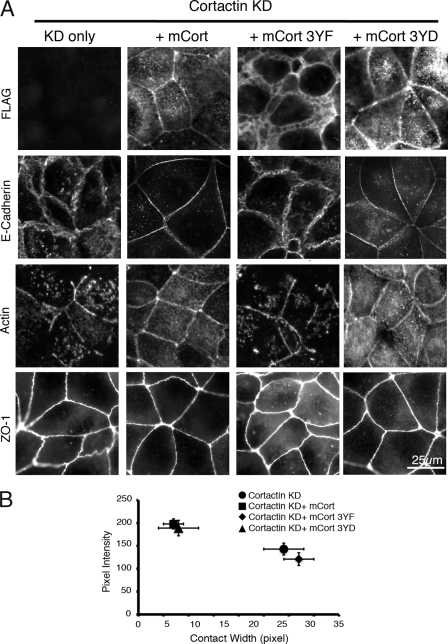
FIGURE 4.
Tyrosine-phosphorylated cortactin is necessary for integrity of E-cadherin-based cell-cell contacts. A, MCF7 cell monolayers were transfected with siRNA against cortactin (cortactin KD). After 72 h, cells were then transfected with plasmids expressing FLAG epitope-tagged wild-type mouse cortactin (mCort) and mouse cortactin with tyrosines 421, 466, and 482 mutated to either phenylalanine (mCort 3YF) or aspartic acid (mCort 3YD). Cells were then fixed and immunostained for cortactin, E-cadherin, F-actin (phalloidin), or ZO-1. Reconstitution with wild-type mouse cortactin restored linear E-cadherin contact integrity as well as perijunctional F-actin staining. Expression of the mouse cortactin 3YF mutant failed to rescue defects in cortactin KD cells, although it remained localized at the cell-cell contacts. Expressing mouse cortactin bearing phosphomimetic mutations (mCort 3YD) restored both E-cadherin integrity and linear junctional F-actin staining. B, E-cadherin-based cell-cell contacts were quantitatively analyzed by measuring E-cadherin contact pixel intensity and contact width as described under “Experimental Procedures.” The intensity and width of E-cadherin staining were restored by reconstitution with wild-type mouse cortactin and cortactin 3YD but not by mouse cortactin 3YF. Data are mean ± S.E. (n = 30).