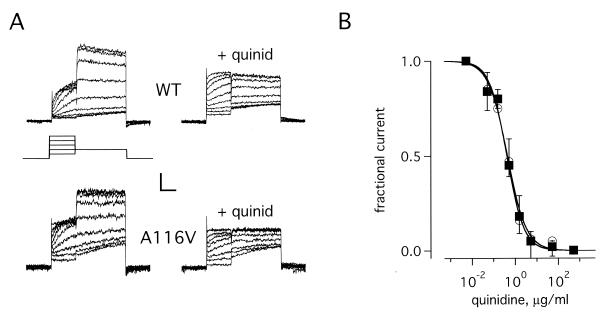
Figure 2.
IKr channels formed with A116V-MiRP1 show wild-type blockade by quinidine. CHO cells expressing wild-type MiRP1 or A116V-MiRP1 and HERG were studied by whole-cell clamp. (A) Whole-cell currents recorded from channels formed with wild-type MiRP1 (WT) and A116V-MiRP1 (A116V) in the absence (left column) or presence of 0.5 μg/ml of quinidine (+quinid). Scale bars represent 50 and 30 pA and 0.7 s for wild type and A116V-MiRP1, respectively. (Inset) Protocol: holding −80-mV, 1-s pulses from −60 to 20 mV in 10-mV steps, 2 s at −40 mV, 1-s interpulse interval. (B) Current–dose relationship for channels formed with wild-type MiRP1 (open circles) and A116V-MiRP1 (filled squares) in the presence of increasing amounts of quinidine. Data from peak currents at −40 mV after a prepulse to +20 mV by using the standard protocol. Theoretical lines were constructed to the function: 1/(1 + H) were H = ([drug]/Ki)n. Ki and n represent the equilibrium dissociation constant and the Hill coefficient, respectively. Fits give values for Ki and n of 0.41 ± 0.04 μg/ml and 1.1 ± 0.1 for wild-type MiRP1 and 0.43 ± 0.06 μg/ml and 1.1 ± 0.2 for A116V-MiRP1; 6 cells in each case.