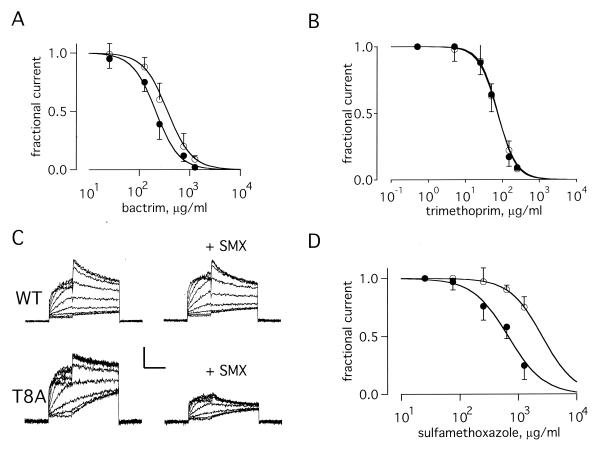
Figure 3.
Channels formed with T8A-MiRP1 are more sensitive to SMX. Currents and fits as in Fig. 2. (A) Current–dose relationship for channels formed with wild-type MiRP1 (open circles) and T8A-MiRP1 (filled circles) in the presence of increasing amounts of TMP/SMX. Data from peak currents at −40 mV after a prepulse to +20 mV by using the standard protocol. Fits give values for wild-type MiRP1 of Ki = 380 ± 40 μg/ml and n = 1.8 ± 0.3 and for T8A-MiRP1 of Ki = 210 ± 30 μg/ml and n = 1.9 ± 0.2; 13 cells in each case. (B) Current–dose relationships in the presence of TMP for wild-type MiRP1 (open circles) and T8A-MiRP1 (filled circles). Fits give values for Ki and n of 71 ± 12 μg/ml and 1.8 ± 0.4 for wild-type MiRP1 and 75 ± 9 μg/ml and 1.9 ± 0.3 for T8A-MiRP1; 5 cells each case. The data thus suggest inhibition was cooperative and two TMP molecules were required to block. (C) Whole-cell currents recorded from channels formed with wild-type MiRP1 (WT) and T8A-MiRP1 (T8A) in the absence (left column) or presence of 633 μg/ml of SMX (+SMX). Scale bars represent 50 pA and 40 pA for wild type and T8A, respectively, and 1 s. (D) Current–dose relationships in the presence of SMX for wild-type MiRP1 (open circles) and T8A-MiRP1 (filled circles). Fits give values for Ki and n of 2,600 ± 200 μg/ml and 1.6 ± 0.6 for wild-type MiRP1 and 675 ± 60 μg/ml and 1.4 ± 0.2 for T8A-MiRP1; 6 cells each case.