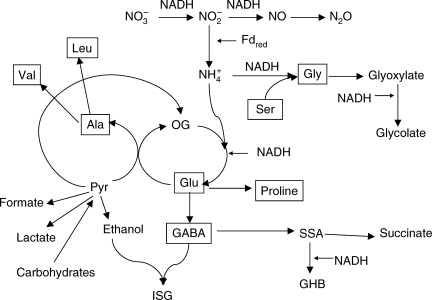
Fig. 3.
Pathways of amino acid turnover in hypoxic conditions. The scheme illustrates connections of nitrite reduction to fermentation pathways operating under hypoxia. The connection of glycolytic fermentation and nitrite reductase-catalysed formation of ammonia occurs mainly via alanine production. Other pathways include lactate, ethanol and formate formation, a link from pyruvate to 2-oxoglutarate (OG) via partial TCA cycle, and the formation of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). GABA can be further converted in mitochondria to succinic semialdehyde (SSA) and then to succinate or γ-hydroxybutyrate (GHB). It can be metabolized via the reaction with ethanol to isosuccinimide-β-glycoside (ISG). Activation of glycine metabolism results in reduction of glyoxylate and formation of glycolate.