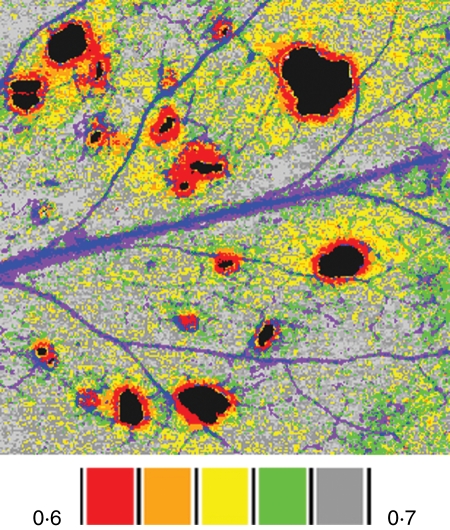
Fig. 2.
False colour images of the location of damage classes surrounding holes in an arabidopsis leaf exposed to herbivory by Trichoplusia ni larvae. Transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana carried a cinnamate-4-hydroxylase (C4H) promoter and β-glucuronidase (GUS) reporter gene fusion. In A. thaliana, enzymes in the phenylpropanoid pathway may contribute to defence against pathogens; C4H is constitutively expressed in the veins of undamaged leaves and induced by wounding near the site of damage. The image was constructed by combining independent images of the same leaf of chlorophyll fluorescence (ΦPSII) and GUS staining for C4H activity using geographic image analysis software. The false-colour scale bars indicate the mean value of ΦPSII for each damage class. The veins shown in blue and purple were classes that were excluded from analysis because their high level of GUS staining was not related to herbivory. Data were generously provided by Dr Jennie Tang.