Figure A1.
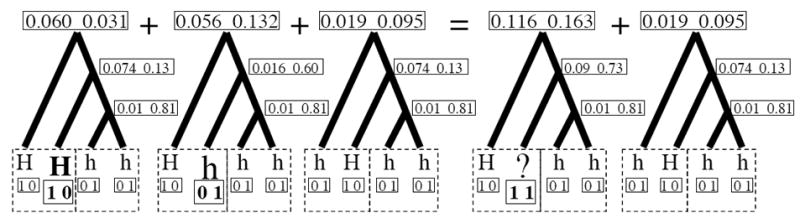
Calculating the probability of unhaplotyped data on coalescent trees. In this example, the left two boxed tips come from an individual displaying the dominant phenotype, and the right two boxed tips from an individual displaying the recessive phenotype. The total data likelihood on the tree is therefore the sum of the data likelihoods of the left three trees. The data likelihood of the first two of these trees can be ‘collapsed’ into the first of the two trees on the right, using ‘H?’ as the haplotype. The data likelihoods are calculated assuming a tree with a total length of three, evenly divided by coalescent events, where the likelihood of an allele remaining the same along a branch of length one is 90%.
