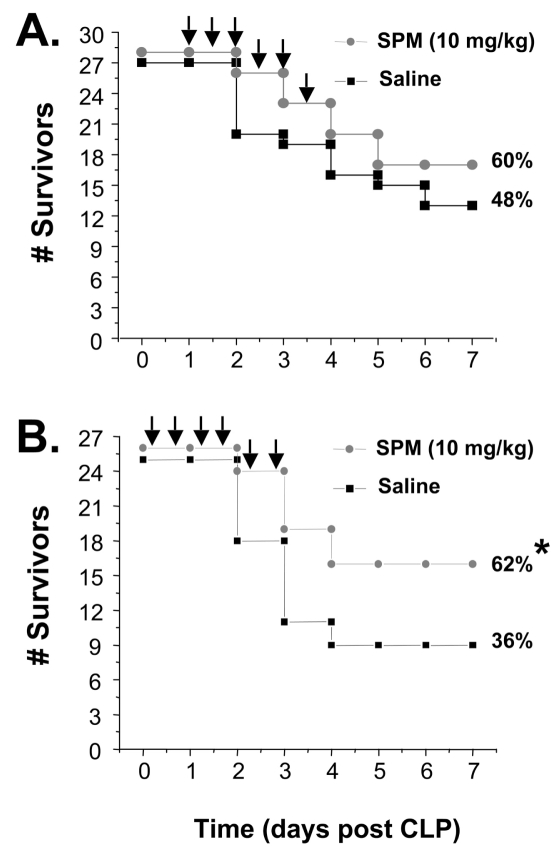
Figure 1.
Spermine protected mice against lethal sepsis. Balb/C mice were subjected to lethal sepsis (induced by CLP), and sper-mine was administered intraperitoneally (i.p., 10 mg/kg, twice a day, for 3 d) beginning at +24 h (A) or +0.5 h (B) post the onset of sepsis. The Kaplan–Meier method was used to compare mortality rates between groups of two independent experiments (with 13–14 mice per group) with similar results. Arrows indicate the time points of spermine administration. *P < 0.05 versus saline control group.