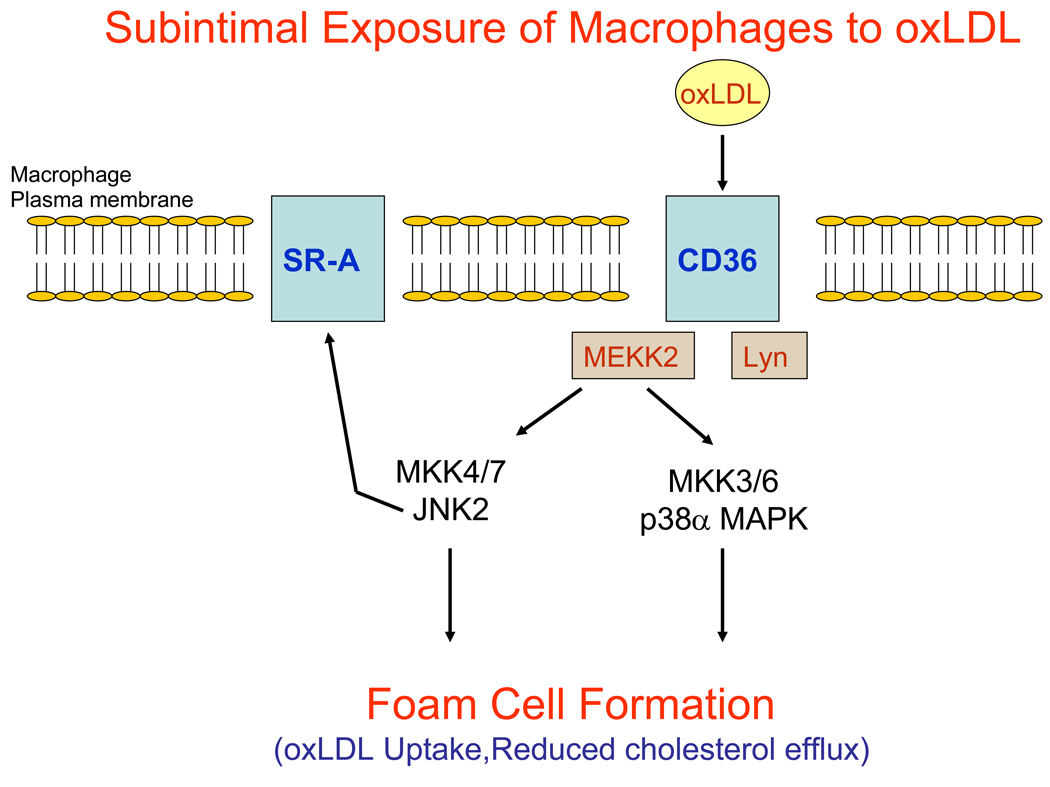
Figure 3.
Simplified model of macrophage foam cell formation in the arterial subintimal space. In response to vascular injury, monocytes are recruited to the intimal surface of arteries where they adhere and invade the vessel, differentiating into macrophages. In the subintimal space, macrophages are exposed to oxidized low density lipoprotein (oxLDL) that binds to the transmembrane protein CD36. Binding of oxLDL to CD36 triggers the activation of src-family kinases such as Lyn and MEKK2. Activation of Lyn and possibly MEKK2 leads to the activation of JNK2 and also p38α MAPK. Through largely undetermined mechanisms, activation of JNK2 and p38α MAPK promote the internalization of oxLDL either via CD36, scavenger receptor A (SR-A) or through other scavenger receptors. JNK2 promotes the phosphorylation of SR-A and this may lead to SR-A internalization while it is associated with modified LDL. Activation of MAPK cascades in macrophages may also modulate cholesterol efflux pathways.