Figure 2. Localization of the B7-1:PD-L1 binding site.
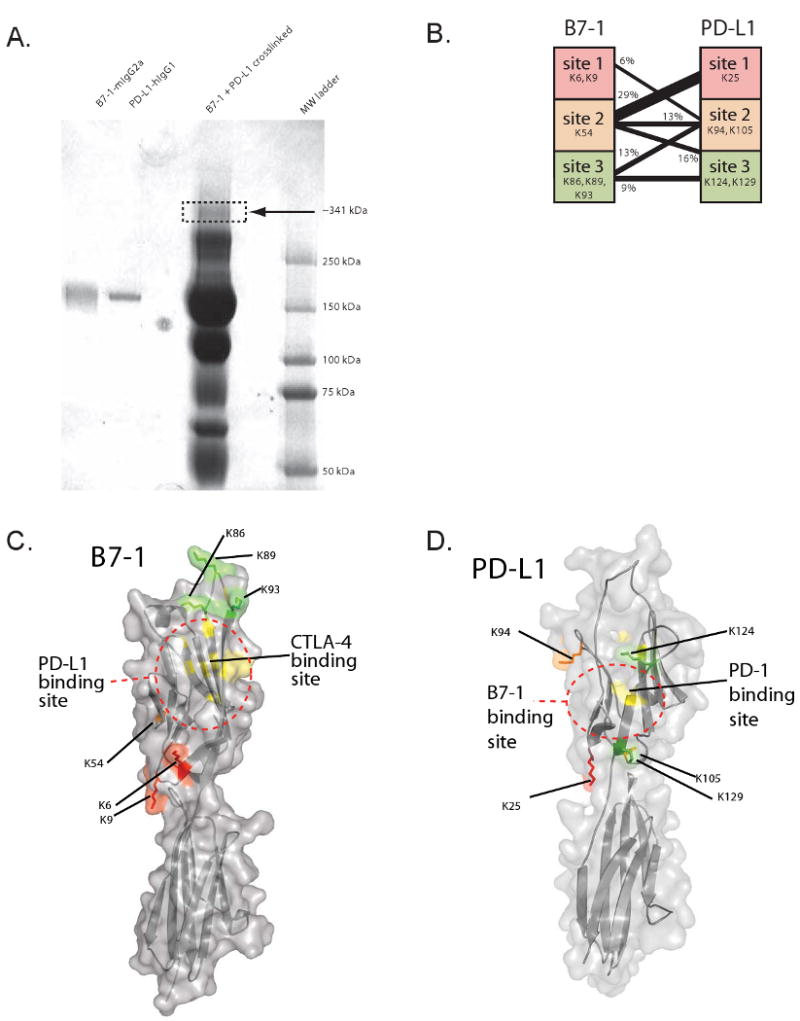
A) B7-1-Ig and PD-L1-Ig and the products of cross-linking with the heterobifunctional crosslinker sulfo-SBED are shown in an SDS-PAGE gel stained with Coomassie Blue. Arrow indicates band of gel that was cut out for mass spectrometric analysis.
B) Peptides were categorized into sites on PD-L1 and B7-1 and grouped according to their lysines. Amino acid numbers start from the position after signal cleavage. The number of distinct peptides containing the sites and the cross-linker were counted and the results are shown graphically.
C and D) Molecular model of (C) B7-1 and (D) PD-L1 showing sites of interaction identified by cross-linking. On each structure, lysines are colored: site 1 lysines are colored red, site 2 lysine(s) are colored orange, and site 3 lysine(s) are colored green. The binding site for CTLA-4 (Stamper et al., 2001) is shown in yellow on the B7-1 model, and the binding site for PD-1 (Wang et al., 2003) is shown in yellow on the PD-L1 model. Dotted lines are shown to summarize the putative B7-1:PD-L1 binding site. There is partial overlap among the B7-1:CTLA-4, B7-1:PD-L1, and PD-L1:PD-1 interfaces.
