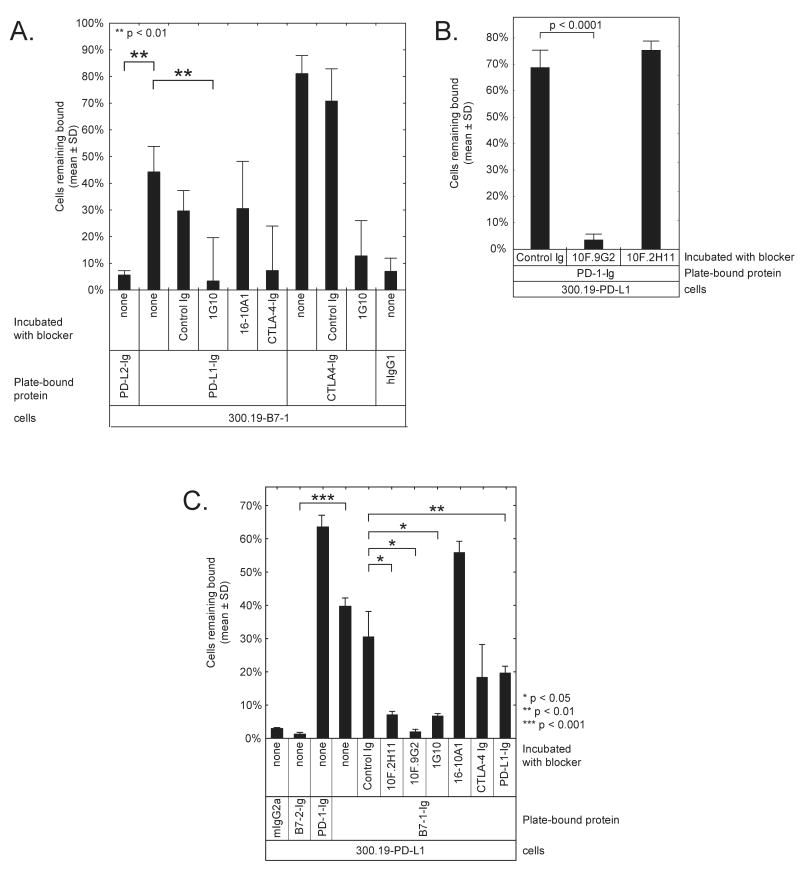
Figure 3. Cell adhesion assay shows specific binding of B7-1 to PD-L1.
A) Adhesion assay with 300.19-B7-1 cells shows specific binding to PD-L1. The mouse pre-B cell line 300.19 was stably transfected with mB7-1 (300.19-B7-1) and labeled with BCECF. Some cells were pre-incubated with 40 μg/mL of anti-B7-1 mAb or CTLA4-Ig, as indicated. Wells were coated with PD-L1-Ig, PD-L2-Ig, CTLA-4-Ig, or hIgG1-Fc and blocked. Fluorescent 300.19-B7-1 cells were introduced into the wells. Fluorescence was measured before and after washing. Untransfected 300.19 cells showed less than 1% binding to similarly coated wells (not shown).
B. Adhesion assay with 300.19 cells stably transfected with mPD-L1 (300.19-PD-L1) demonstrates the differential ability of two anti-PD-L1 mAbs to block the interaction between PD-L1 and PD-1.
C. Adhesion assay with 300.19-PD-L1 cells shows specific binding to B7-1. Wells were coated with B7-1-Ig, B7-2-Ig, PD-1-Ig, or hIgG1-Fc and blocked, then some cells were incubated with 20 μg/mL of the indicated mAbs. 300.19-PD-L1 cells were labeled with BCECF, introduced into the wells, and fluorescence was measured before and after washing. Untransfected 300.19 cells showed less than 4% binding (not shown).