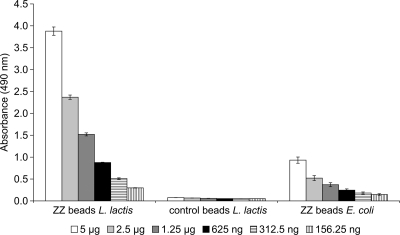
FIG. 2.
ELISA demonstrating specific binding of IgG to ZZ domain-displaying beads isolated from L. lactis; ZZ beads L. lactis indicates beads isolated from L. lactis NZ9000(pNZ-ZZCAB) that produce ZZ-PhaC; control beads L. lactis indicates granules isolated from L. lactis NZ9000(pNZ-CAB) that produce PhaC only; and ZZ beads E. coli indicates granules isolated from E. coli producing ZZ-PhaC. Isolated PHB granules were bound to ELISA plates, and HRP-conjugated rabbit anti-mouse IgG was used to detect the functional display of the ZZ domain. o-Phenylenediamine was used as the substrate for HRP. L. lactis-derived wild-type granules not displaying the ZZ domain and ZZ domain-displaying granules from E. coli were used as negative and positive controls, respectively. The increasingly darker gray shading of the columns indicates decreasing amounts of granule protein used in the assays (5 μg, 2.5 μg, 1.25 μg, 625 ng, 312.5 ng, and 156.25 ng). Measurements were performed in triplicate, and the mean values and standard deviations are indicated.