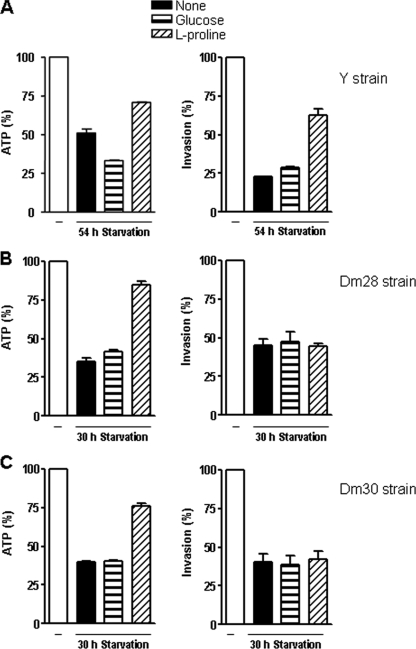
FIG. 6.
Effect of l-proline on ATP production and infectivity of different T. cruzi strains. Metacyclic forms of the indicated strains were subjected to nutritional stress for 54 h (Y strain) or 30 h (Dm28 and Dm30 strains) and were thereafter incubated for 1 h with glucose (1 mM), l-proline (0.75 mM or 3.0 mM), or l-glutamic acid (1 mM). After washings, the parasite ATP content and the ability to enter HeLa cells were examined. Intracellular parasite numbers were counted in 250 cells stained with Giemsa. A reference value of 100% was assigned to controls. Values represent the means ± standard deviations of the results of one representative experiment out of three experiments performed. The differences in ATP content and infectivity of 54-h-starved and l-proline-supplemented Y strain parasites were significant (P < 0.0005). With regard to the Dm28 and Dm30 strains, the differences in the levels of ATP content of 30-h-starved and l-proline-supplemented parasites were significant (P < 0.0001).