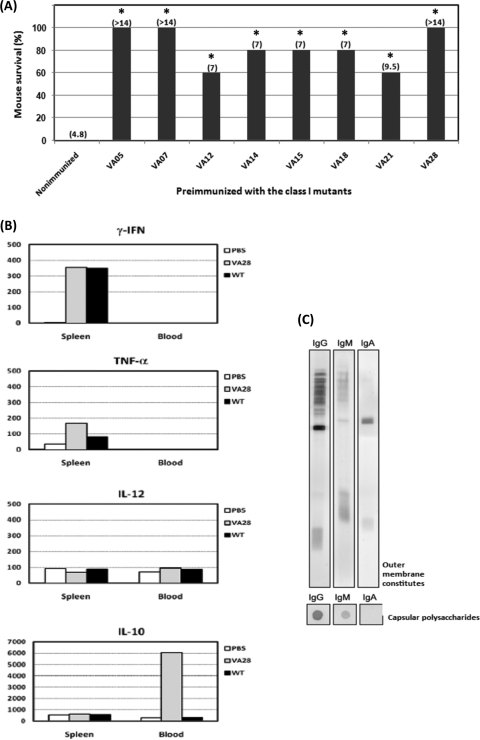
FIG. 5.
Characterization of the avirulent yet immunogenic class I mutant strains. (A) Oral administration with the class I mutants allowed mice to survive challenge with wild-type K. pneumoniae infection. Five BALB/c mice were orally administered a single dose of 107 CFU of a particular class I mutant strain. The preimmunized mice, together with age-matched naïve mice, were challenged with 107 CFU of wild-type K. pneumonia 6 weeks later. The survival rate of the infected mice was monitored daily for 2 weeks. MDD are shown in parentheses, and both mortality rate and MDD were determined by Kaplan-Meier analysis. Sera from all mice were collected 1 day prior to challenge with the wild-type strain and were used to detect the production of K. pneumoniae-specific antibodies. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01. Statistical significance was determined by comparison of survival curves by use of the log rank test (Kaplan-Meier analysis; Prism4). (B) Cytokine production upon oral administration with the class I mutant VA28. Sera and spleens were collected at 24 hpi and were analyzed for cytokine production by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The mean production levels of cytokines (gamma interferon, tumor necrosis factor alpha, IL-12, and IL-10) in five mice per group are shown in pg per 100 μg of total proteins. (C) Specific antibodies against the outer membrane constituents and capsular polysaccharides of K. pneumoniae were detected in pooled antisera from the five mice that were preimmunized with VA28.