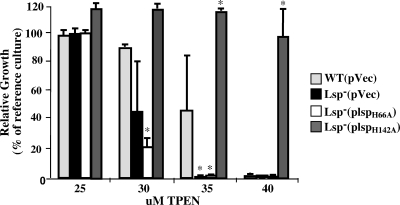
FIG. 4.
Hypo- and hyperresistance to zinc starvation results from mutation of binding site residues. The importance of several histidine residues of the predicted Lsp metal-binding site was evaluated by alanine substitution mutagenesis. Plasmids expressing the altered alleles (pLspH66A and pLspH142A) were introduced into the Lsp− mutant and their ability to promote growth following the addition of the indicated concentrations of TPEN then compared to growth of the wild-type (WT) or Lsp− strain, both of which contained the empty pABG5 vector (pVec). Culture for all assays was conducted in medium supplemented with chloramphenicol. Growth is presented relative to that of WT(pVec) grown in the absence of TPEN and antibiotic (reference culture). The data reported represent the means and standard errors of the means derived from at least two independent experiments. Asterisks represent P values of <0.05.