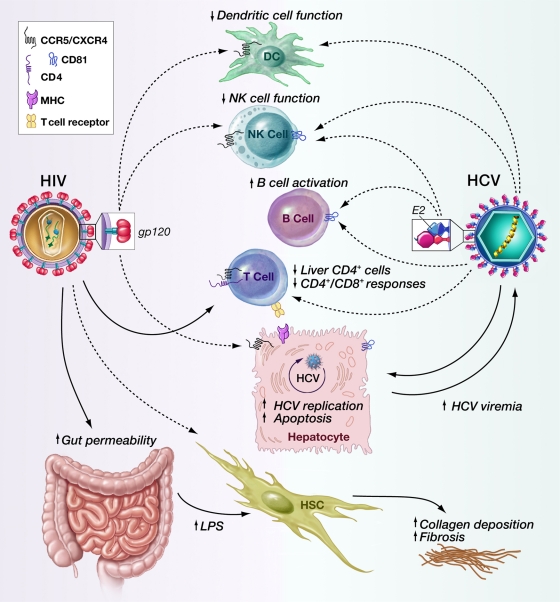
FIG. 1.
Mechanism of HCV-HIV interaction. HIV does not infect hepatocytes but can influence the outcome of HCV infection through infection of CD4+ T cells and the effects of gp120 protein on hepatocytes and other immune cells via its interaction with chemokine receptors. HIV infection of gut-associated lymphoid tissue leads to increased LPS uptake, resulting in HSC activation and increased fibrosis. Possible HIV infection of HSCs can also lead to HSC activation. The effects of HCV on immune cells may affect the outcome of HIV infection. DC, dendritic cell; MHC, major histocompatibility complex. Dashed arrows represent the effect of viral envelope proteins or possible infection; solid arrows represent productive infection.