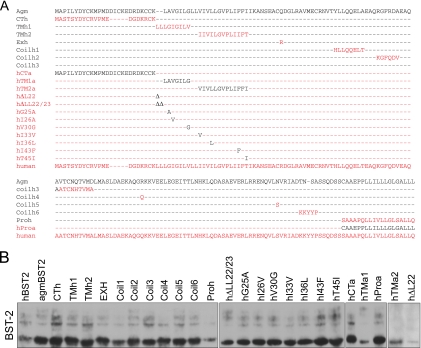
FIG. 3.
Deletion of 22-LL-23 from hBST-2 causes resistance to HIV-1 Vpu. (A) Illustration of the BST-2 mutations studied. HBST-2 and agmBST-2 sequences are shown in red and black letters, respectively. (B) The BST-2 DNA constructs (200 ng) were transfected into HEK293T cells. Expression of BST-2 proteins was assessed by Western blotting with anti-Flag antibody. (C, D) Effects of BST-2 proteins on the production of wild-type HIV-1. HEK293T cells were transfected with various amounts of BST-2 DNA (0, 10, 20, 50, 100, and 200 ng) together with 100 ng of BH10 DNA. Levels of infectious viruses were determined by infecting TZM-bl indicator cells and then measuring luciferase activity (C) or by measuring viral reverse transcriptase activity (D). (E) All BST-2 DNA constructs were tested in one transfection experiment with 100 ng of BST-2 DNA together with 100 ng of BH10 DNA. Levels of infectious HIV-1 particles in the culture supernatants were determined in a single-cycle infection assay by infecting TZM-bl indicator cells. (F) Effects of BST-2 proteins on the production of virus-like particles from GPV-CTEx4 DNA in the absence of Vpu. HEK293T cells were transfected with 50 ng of each BST-2 DNA together with 200 ng of GPV-CTEx4 DNA. Amounts of viruses in culture supernatants were determined by measuring viral reverse transcriptase activity. Expression of viral Gag in the cells was assessed by Western blotting. CPM, counts per minute; RLU, relative luciferase units.