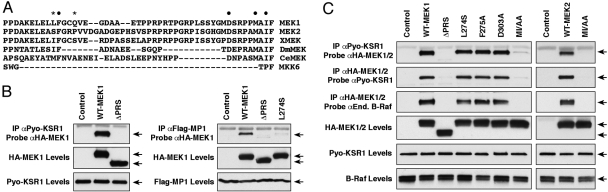
Fig. 1.
Identification of PRS residues in MEK1/2 required for KSR1 and B-Raf binding. (A) Alignment of PRS sequences from rat MEK1 and MEK2 and MEK homologs in Xenopus, Drosophila, and C. elegans. Human MKK6, which lacks the PRS, is also shown. ●, indicates conserved PRS residues examined in this study; *, indicates residues required for the MEK1/MP1 interaction. (B) WT-KSR1 MEFs were transfected with HA-WT- or ΔPRS-MEK1 (deletes residues 270–307) constructs. CCL39 cells were cotransfected with constructs encoding Flag-MP1 and HA-WT-, ΔPRS-, L274S-MEK1 or vector control. The KSR1 and MP1 scaffolds were immunoprecipitated and examined for MEK1 binding by immunoblot analysis. (C) Various HA-MEK1 or MEK2 proteins were expressed in WT-KSR1 MEFs, and the MEK/KSR1 and MEK/B-Raf interactions were detected by coimmunoprecipitation and immunoblot analysis.