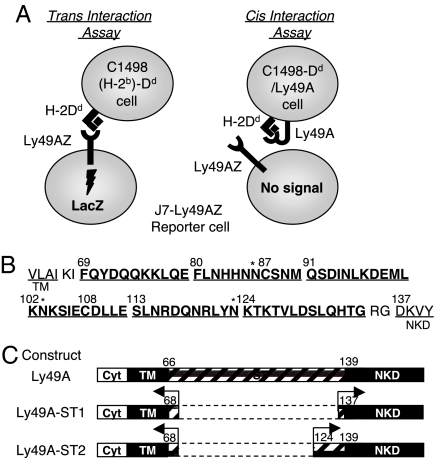
Fig. 1.
Ly49A reporter assays and the stalk-deletion mutant Ly49As. (A) Schematic representation of reporter cell assays to detect cis and trans binding of Ly49A and ligand. In both assays, successful engagement of ligand by reporter cells expressing Ly49AZ or various Ly49AZ mutants induces LacZ expression. (Left) Trans interaction assay. A positive readout indicates reporter cell receptor binding to ligand on a target cell (trans interaction) and subsequent signal transduction. (Right) Cis interaction assay. Ly49A expressed on target cells binds to H2Dd on the same cell (cis interaction); thus, masking the trans-recognition by wild-type reporter cells expressing Ly49A. Various Ly49A mutant receptors were expressed on the target cells. A negative response by reporter cells indicates that the receptor on target cells cis interacts with ligand on the same target cell. (B) The amino acid sequence of the stalk region is arbitrarily divided into 6 segments that correspond to the sites deleted from Ly49A mutant receptors. Two cysteines are located at 87 and 108. Three potential N-glycosylation sites are marked with an asterisk. (C) Schematic representation of stalk-deletion mutant Ly49A-ST1 and Ly49A-ST2 receptors. TM, transmembrane; Cyt, cytoplasmic; ST, stalk region.