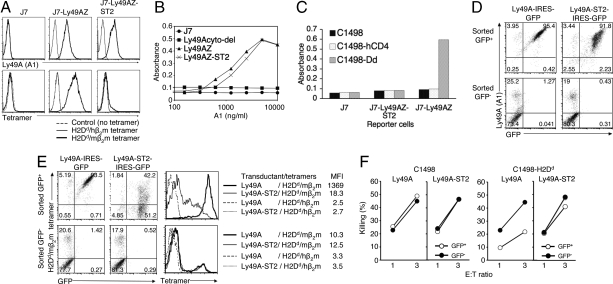
Fig. 3.
Essential role of Ly49A stalk region for the trans interaction. (A) Expression level of Ly49A and Ly49A-ST2 on J7 reporter cells, as determined by anti-Ly49A mAb (A1) (Upper), and H2Dd/mβ2m tetramers binding to reporter cells expressing Ly49A-ST2 (Lower). Ly49A-ST2 was transduced with lentivirus, and selected with the same dose of puromycin as for J7-Ly49AZ selection. Indicated reporter cells were stained with SA-PE-conjugated H2Dd/mβ2m or H2Dd/hβ2m tetramers. (B) Signaling ability of Ly49A-ST2 by mAb cross-linking. Indicated doses of A1 mAb (100 μL) were immobilized in a 96-well plate overnight. Cells (1 × 105) of each reporter cell line were plated and incubated overnight. CPRG assays were then performed. (C) Trans interaction assays with reporter cells expressing Ly49A-ST2. Indicated target and reporter cells were incubated overnight and subjected to CPRG assays. (D and E) B6 BM progenitor cells were transduced with retrovirus encoding the indicated constructs to make BM chimera with B6 mice. Forty days after the transplantation, LAK cells were generated. CD3-negative LAK cells were sorted into 2 populations by GFP expression, and stained with anti-Ly49A mAb (A1) for D, and H2Dd/mβ2m tetramers for E. MFI of tetramer bindings in each transductant is shown (E). FACS profiles of LAK cells after FACS-sorting by GFP are shown in D. (F) Killing assays were performed with indicated target and sorted LAK cells.