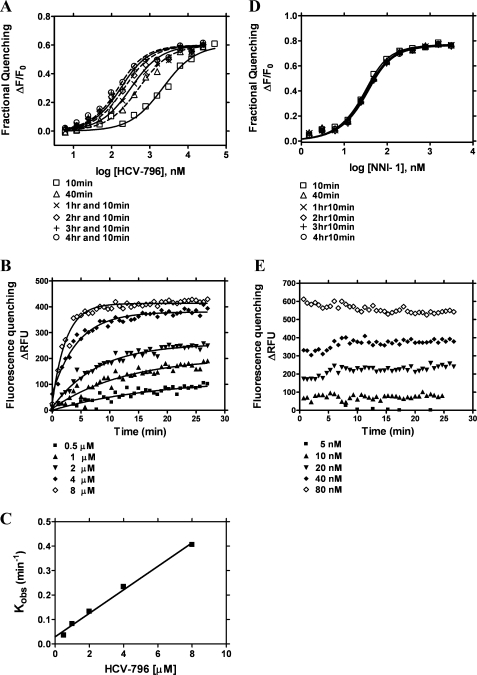
FIGURE 4.
The binding of HCV-796 to NS5B570-Con1 in the fluorescence quenching binding assay. The binding experiments were performed in the absence of HCV cIRES RNA. A, the binding of HCV-796 with NS5B570-Con1 at 10 min, 40 min, 1 h 10 min, 2 h 10 min, 3 h 10 min, and 4 h 10 min. The Kd values are shown in Table 2. B, equilibrium of HCV-796 binding to NS5B570-Con1. Progress toward the binding equilibrium was assessed every 40 s, and concentrations of HCV-796 were 0.5, 1, 2, 4, and 8 μm. C, the rate of NS5B binding as a function of HCV-796 concentrations. The dissociation rate constant (koff) was derived from nonlinear regression curve fitting to Equations 4 and 5, and the t½ was calculated from Equation 6 (see “Experimental Procedures”). The koff value of HCV-796 was 4.9 ± 0.5 × 10−4 s−1, and the t½ was 25 ± 6 min (n = 3). D, the binding of NNI-1 with NS5B570-Con1 at the binding equilibrium of 10 min, 40 min, 1 h 10 min, 2 h 10 min, 3 h 10 min, and 4 h 10 min. E, the equilibrium of NNI-1 binding to NS5B570-Con1. Fluorescence quenching, which indicated progress toward binding equilibrium, was measured every 40 s. Concentrations of NNI-1 were 5, 10, 20, 40, and 80 nm.