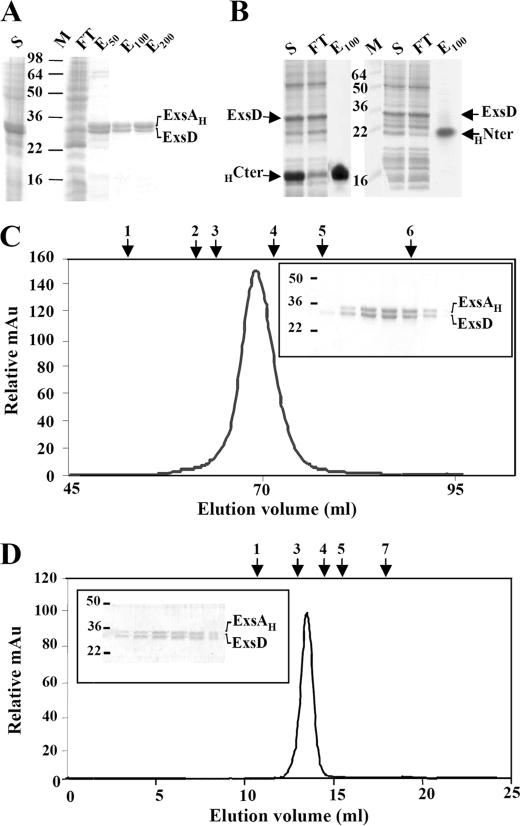
FIGURE 3.
Copurification of the ExsAH protein and its anti-activator ExsD. SDS-PAGE analysis of nickel affinity chromatography of coproduced ExsAH-ExsD (A), HCter (HExsA(166–268))-ExsD (B, left panel), and HNter (HExsA(1–168))-ExsD (B, right panel). S, supernatant obtained after ultracentrifugation; M, protein marker (kDa); FT, flow-through; E50, E100, E200, proteins eluted at 50, 100, and 200 mm imidazole, respectively. The gels were stained by Coomassie Blue. C, elution profile of the ExsAH-ExsD complex on size exclusion chromatography (Hiload 16/60 Superdex 200); the complex elutes as a single peak at 69.13 ml. The inset represents the SDS-PAGE monitoring the eluted proteins from 66 to 72 ml. D, elution profile of the ExsAH-ExsD complex on analytical size exclusion chromatography (Superdex 200 10/300 GL); the complex elutes as a single peak at 14.1 ml. The inset represents the SDS-PAGE monitoring the eluted proteins from 13.5 to 15.25 ml. Above the two chromatograms are indicated the elution volumes of the standard proteins with known molecular weight and Stoke radius: arrow 1, ferritin (440 kDa, 61 Å); arrow 2, catalase (232 kDa, 52.2 Å); arrow 3, aldolase (158 kDa, 48.1 Å); arrow 4, bovine serum albumin (67 kDa, 35.5 Å); arrow 5, ovalbumin (43 kDa, 30.5 Å); arrow 6, chymotrypsinogen (25 kDa, 20.9 Å); arrow 7, ribonuclease A (13.7 kDa, 16.4 Å).