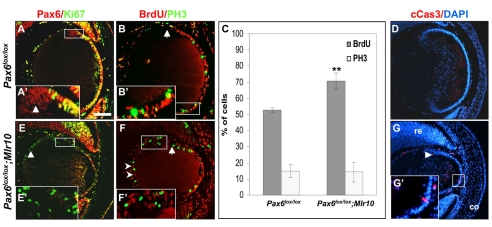
Fig. 3.
Pax6-deficient lens epithelium fails to exit the cell cycle at the lens equator and undergoes apoptosis. (A-B′,E-F′) Antibody labeling of control (A,B) and Pax6lox/lox;Mlr10 (E,F) lenses from E14.5 mouse embryos. (A,E) Expression of Pax6 (red) and Ki67 (green) with co-expression in the lens epithelium (LE) of Ki67 and Pax6 (A, yellow). Some Ki67- cells express Pax6 (A′, arrowhead). In Pax6lox/lox;Mlr10, Pax6- Ki67+ cells are detected in the transitional zone (E′) and in the posterior lens (E, arrowhead). (B,F) Phosphohistone H3 (PH3, green) and BrdU (B,F, red) were detected in the Pax6lox/lox LE up to the lens equator (arrow, B) but also posterior to the lens equator in the Pax6lox/lox;Mlr10 lenses (F,F′) and in the posterior lens (F, arrowheads). (C) Quantitative analysis reveals a significant increase in the percentage of BrdU+ cells in Pax6lox/lox;Mlr10 lenses (70.7±5.1% s.d.) as compared with the control LE (52.8±1.4%, **P<0.001). The percentage of PH3+ cells is not altered in the Pax6- LE (control 14.3±6.2%; mutant 14.7±4.1%). (D,G,G′) Cleaved caspase 3 (cCas3)-positive cells detected in the LE of Pax6lox/lox;Mlr10 lenses (G,G′, red, arrowhead) but not in the control E14.5 mouse embryo (D). Counterstaining is with DAPI (blue). co, cornea; re, retina. Scale bar: 100 μm.