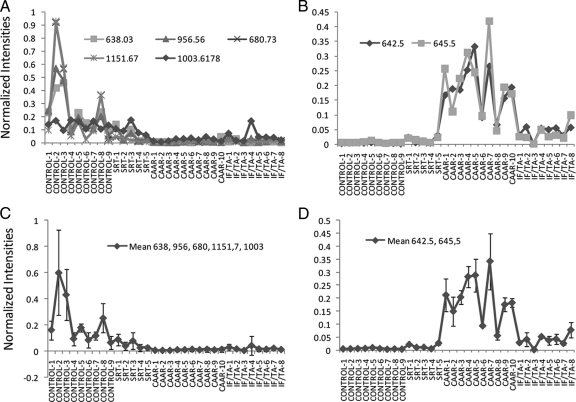
Fig. 5.
Specific peptides are potential biomarkers for the diagnosis of chronic allograft dysfunction. A, normalized ionic intensities of individual peptides derived from uromodulin and kinin present higher levels in control than in CAD urines. B, normalized intensities of individual unknown ions show higher levels in control than in CAD urines. C, mean ± S.D. expression of peptides shown in A. Kruskal-Wallis test was significant at p < 0.0001. The difference between control subtypes versus CAD subtypes was significant at p < 0.0001. The means within control and CAD subgroups were not significant (p > 0.05). D, means of ions shown in B. The data were significantly different (p < 0001, Kruskal-Wallis test). The differences between CAD and control means were significant at p < 0.0001. The means of CAAR versus IF/FA were also significantly different (p < 0.0001).