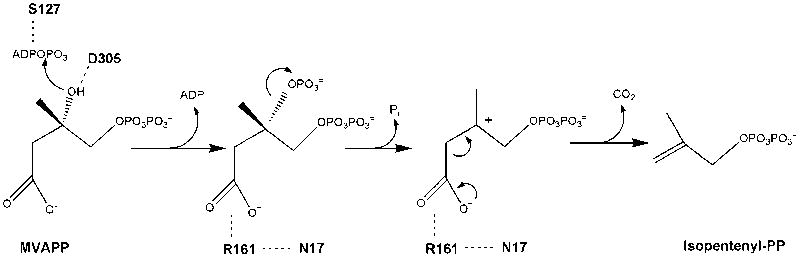
Figure 7.
Proposed human MDD active site residues and MDD reaction chemistry. D305 is shown juxtaposed to MVAPP’s C3 hydroxyl, which is consistent with this residue’s large functional contribution [8] and its positional homology with the general base catalyst in the active site of mevalonate kinase [11]. Similar observations [10, 12] suggest that hMDD’s S127 interacts with ATP to orient the phosphoryl chain for productive gamma phosphoryl transfer to MVAPP. Observations of impaired binding of MVAPP analogues by N17A and a large diminution in catalytic efficiency for R161Q are interpreted in the context of structural models to implicate these residues in interaction with the C1 carboxyl of MVAPP. Four chemical species involved in the reaction pathway (from left to right) include: substrate MVAPP; a transient 3-phosphoMVAPP intermediate (in which the C3 alcohol is transformed to the improved leavind group needed to produce the next intermediate); a transient beta carboxy carbenium intermediate (providing an electon sink to drive the decarboxylation reaction); reaction product isopentenyl diphosphate. The participation of a carbocation intermediate is suggested by the potency of MDD inhibition by MVAPP analogs with positively charged atoms corresponding to MVAPP’s C3 (e.g. diphosphoglycolyl proline [17]; Fig. 6A).