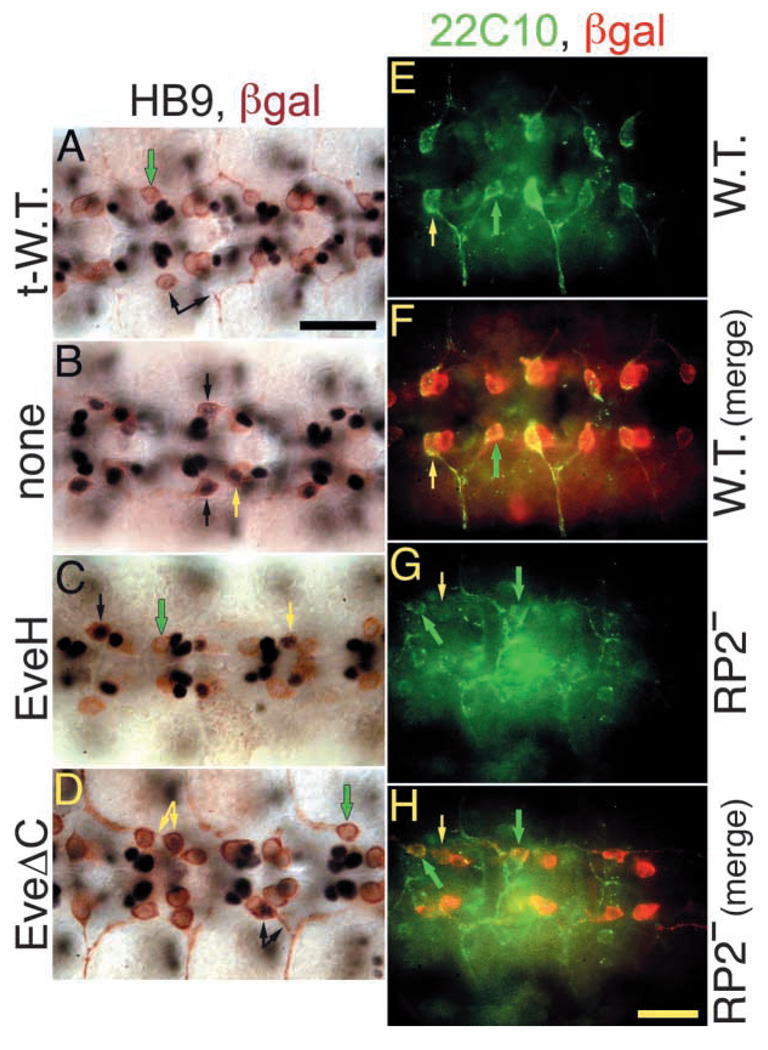
Fig. 8.
In RP2 and aCC neurons lacking eve function, derepression of Drosophila Hb9 expression correlates with mutant axonal morphology, and expression of 22C10 antigen is reduced. All embryos carry both the RN2-Gal4 and UAS-τlacZ transgenes. (A–D) Drosophila Hb9 expression with varying degrees of rescue of the RP2 mutant; anti-Hb9 staining (black) followed by anti-β-gal staining (brown). Scale bar in A (black): 20 µm. (A) Wild-type-Eve rescued embryos. Note that Hb9 is not expressed in neurons that have a normal axonal morphology (green arrow), while RP2s that extend an axon posteriorly (abnormally) have weak Hb9 expression (arrows). (B) ΔRP2A mutant. Note that both RP2s (black arrows) and aCCs (yellow arrow) ectopically express Hb9 (although pCCs do not). (C) ΔRP2A mutant rescued with one copy of the EveH transgene (expressing the Eve HD only, see Fig. 6C). Note that many RP2s (black arrows) and aCCs (yellow arrow) ectopically express Hb9, but some RP2s do not (green arrow). (D) ΔRP2A mutant rescued with one copy of the EveΔC transgene (expressing Eve without its Gro-dependent repressor domain, see Fig. 6D). Note that Hb9 is derepressed in the subset of neurons that show abnormal axonal phenotypes (RP2, black arrows; aCC, yellow arrows), but not in those that show a normal axonal morphology (green arrow; see text for more details). (E,F) In wild-type embryos, 22C10 antigen (green staining in E–H) is expressed in aCC (yellow arrow) and RP2 (green arrow), but not in pCC (which is immediately posterior to each aCC and stains only for β-gal, red in F; F is a merged image of 22C10 and β-gal staining, so that the overlap appears yellow, here and in H). (G,H) in the ΔRP2A mutant, expression of 22C10 antigen is reduced relative to the wild type, especially in aCC (yellow arrow), but probably also in RP2 (green arrows). Scale bar in H (yellow): 20 µm in E–H.