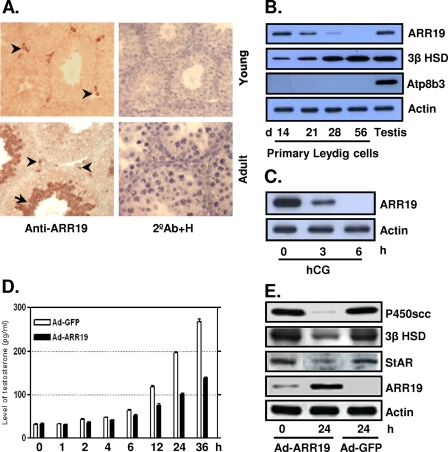
FIGURE 1.
Expression of ARR19 in testicular Leydig cells and its function as a steroidogenic control factor. A, ARR19 expression was detected in the interstitial compartment in 14-day-old mouse testis (Young) and in a subset population of the interstitial cells in 56-day-old testis (Adult). ARR19 was also expressed within seminiferous tubules (haploid spermatids) in 56-day-old testis (Adult). The arrowheads indicate cells that express ARR19 within the interstitial region, and an arrow indicates ARR19-expressing germ cells. 2°Ab+H, immunocytochemistry with the secondary antibody (2°Ab) only for a negative control along with nuclear staining with hematoxylene (H). B, ARR19 expression was down-regulated during the development of Leydig cells. Primary Leydig cells were isolated from 14-, 21-, 28-, and 56-day-old mouse testes, and Western blot analyses were subsequently performed. Atp8b3 is a germ cell marker that is used to check for cross-contamination. C, ARR19 expression was down-regulated by LH (hCG) signaling. 14-day-old mice were injected with hCG for 0–6 h, followed by Western blot analyses of whole testis extracts. D, testosterone biosynthesis was inhibited by adenovirus-mediated overexpression of ARR19 (Ad-ARR19). R2C cells, which were grown in media supplemented with 15% charcoal-stripped serum, were infected with Ad-ARR19 or control Ad-GFP virus, and media were collected at different time points (0–36 h) for radioimmune assays. E, the expression of steroidogenic enzyme genes was inhibited by ARR19 overexpression in R2C cells. R2C cells were infected with Ad-ARR19 and control Ad-GFP for 24 h. The whole cell proteins were extracted, followed by Western blot analysis with anti-P450scc, anti-3β HSD, and anti-StAR antibody.