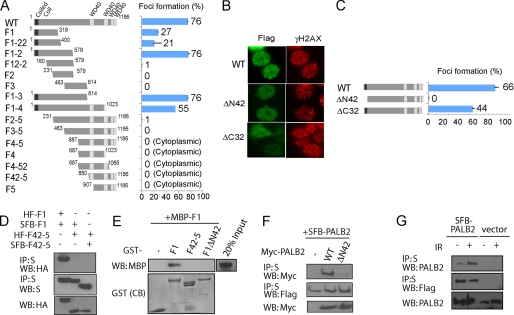
FIGURE 3.
PALB2 focus formation at DSBs requires its N terminus. A, HEK293T cells transfected with plasmids encoding SFB-tagged wild type (WT) or deletion mutants of PALB2 were exposed to 10 Gy of ionizing radiation. Cells were fixed, and immunostaining was performed with anti-FLAG and anti-pH2AX antibodies. The percentage of cells showing foci overlapping with γH2AX was plotted. B, foci accumulation of wild type and PALB2 internal deletion mutants. The percentage of foci positive cells was plotted in C. D, co-immunoprecipitation (IP) experiments using hemagglutinin (HA)-FLAG-tagged and SFB-tagged PALB2 F1 and F42–5 fragments were performed (5% input was showed). WB, Western blot. E, recombinant GST and MBP-tagged PALB2 fragments were subjected to pulldown assays. CB, Coomassie Blue staining. F, Myc-tagged wild-type and ΔN42 PALB2 mutant were subjected to co-immunoprecipitation experiments along with wild-type SFB-tagged PALB2 (5% input was showed). G, 293T cells stably expressing SFB-PALB2 or vector alone were mock-treated or irradiated. Cell lysates were subjected to S beads pulldown (5% input was showed). The amounts of SFB-tagged and endogenous PALB2 presented in the precipitates were determined by Western blotting analyses using anti-FLAG or anti-PALB2 antibodies.