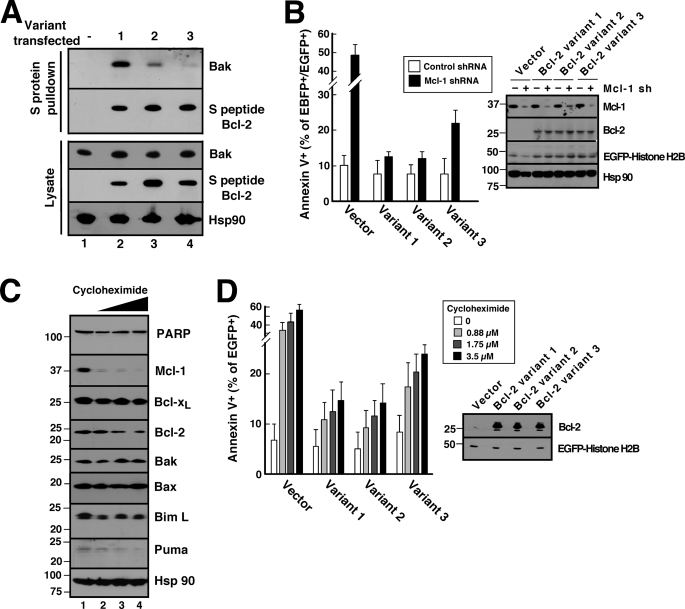
FIGURE 5.
Different Bcl-2 variants exhibit different abilities to protect against Mcl-1 knockdown- and cycloheximide-induced apoptosis in Jurkat cells. A, 24 h after transient transfection with S peptide-tagged Bcl-2 variants, cell lysates prepared in CHAPS buffer were reacted with S protein-agarose to recover Bcl-2 complexes. Pulldowns were probed with anti-Bak antibody and, as a control, anti-S peptide antibody. B, 48 h after co-transfection with empty vector (pCMS5C expressing EBFP-histone H2B) or pCMS5C-Mcl-1-shRNA and pCMS5A vector (pCMS5A expressing EGFP-histone H2B), pCMS5A-Bcl-2 variant 1, pCMS5A-Bcl-2 variant 2, or pCMS5A-Bcl-2 variant 3, Jurkat cells were collected and stained with APC-annexin V. The percentage of EBFP+EGFP+ cells stained with annexin V is indicated. Error bars, mean ± S.D. of three independent experiments. A representative experiment is shown in supplemental Fig. S5. Inset, whole cell lysates from one of the experiments subjected to immunoblotting. C, after Jurkat cells were treated for 24 h with diluent (0.1% DMSO, lane 1) or cycloheximide at 0.88, 1.75, and 3.5 μm (lanes 2–4, respectively) in the presence of 5 μm Q-VD-OPhe to inhibit caspase activation, whole cells lysates were subjected to SDS-PAGE, transferred to nitrocellulose, and probed with antibodies to the indicated polypeptide. Hsp90 served as a loading control. PARP, poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. D, 24 h after transfection with pCMS5A, pCMS5A-Bcl-2 variant 1, pCMS5A-Bcl-2 variant 2, or pCMS5A-Bcl-2 variant 3, Jurkat cells were treated with the indicated concentration of cycloheximide for another 24 h and then stained with APC-annexin V. The percentage of EGFP+ cells stained with annexin V is indicated. Error bars, mean ± S.D. of three independent experiments. A representative experiment is shown in supplemental Fig. S6. Inset, whole cell lysates from one of the experiments subjected to immunoblotting.