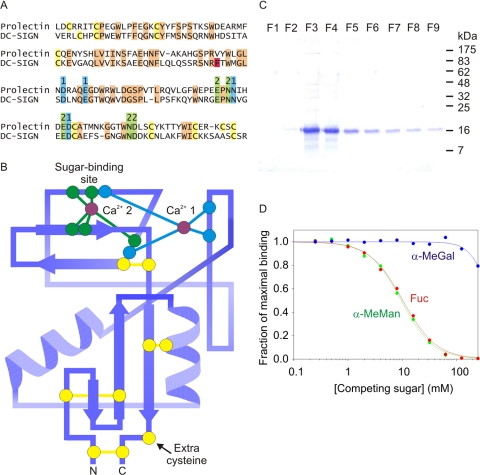
FIGURE 2.
Characterization of the CRD in prolectin. A, sequence comparison between the CRDs of DC-SIGN and prolectin, with cysteine residues highlighted in yellow, ligands for Ca2+ 1 and 2 highlighted in blue and green, and other conserved residues shaded orange. Phe325 of DC-SIGN, which forms a critical part of the secondary binding site, is highlighted in red. B, diagram of the proposed topology of the CRD from prolectin, based on the structure of the CRD from DC-SIGN (Protein Data Base entry 1K9I). Conserved residues are highlighted in the same colors as in A. C, gel showing purification of the extracellular domain of prolectin expressed in E. coli. Aliquots of fractions eluted from a mannose-Sepharose affinity column with EDTA were run on the gel, which was stained with Coomassie Blue. D, examples of solid-phase binding competition assays using monosaccharides to inhibit binding of 125I-Man-BSA (radiolabeled, mannose-conjugated bovine serum albumin) to the extracellular domain of prolectin immobilized in polystyrene wells.