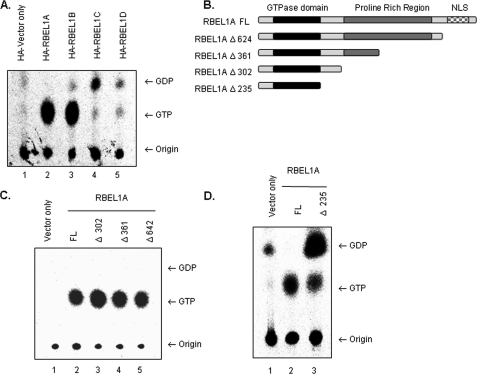
FIGURE 4.
A, GTP/GDP binding properties of the RBEL1 isoforms. HA tag vector only (lane 1) serves as a negative control for background levels nucleotide binding. The GTP/GDP binding assays for HA-tagged RBEL1A (lane 2), RBEL1B (lane 3), RBEL1C (lane 4), and RBEL1D (lane 5) were performed as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Arrows indicate migration of GTP or GDP; the bottom arrow points to the origin of samples. B, schematic diagram of truncation constructs used in the GTPase assays in panels C and D. Truncations of the C terminus of full-length RBEL1A (RBEL1A FL) are as follows: RBEL1A Δ624 truncates RBEL1A at amino acid 624. The RBEL1A truncation at amino acid 361 (RBEL1A Δ361) eliminates half of RBEL1A's proline-rich region. The resulting protein product encodes the region of RBEL1A that is identical to RBEL1B. Truncation at amino acid 302 (RBEL1A Δ302) eliminates the rest of the proline-rich region. The deletion construct, RBEL1A Δ235, encodes the N-terminal core GTPase domain that is identical among all the isoforms. C, GTPase assays comparing the GTP/GDP-binding potential of full-length HA-RBEL1A (lane 2), RBEL1A Δ302 (lane 3), RBEL1A Δ361 (lane 4), and RBEL1A Δ624 (lane 5). Immunoprecipitation of HA-vector only (lane 1) served as a negative control. D, GTPase assays of the core GTPase domain of RBEL1 (RBEL1A Δ235, lane 3) and full-length RBEL1A (lane 2); HA-tag vector only (lane 1) serves as a negative control for background levels GTP and GDP.