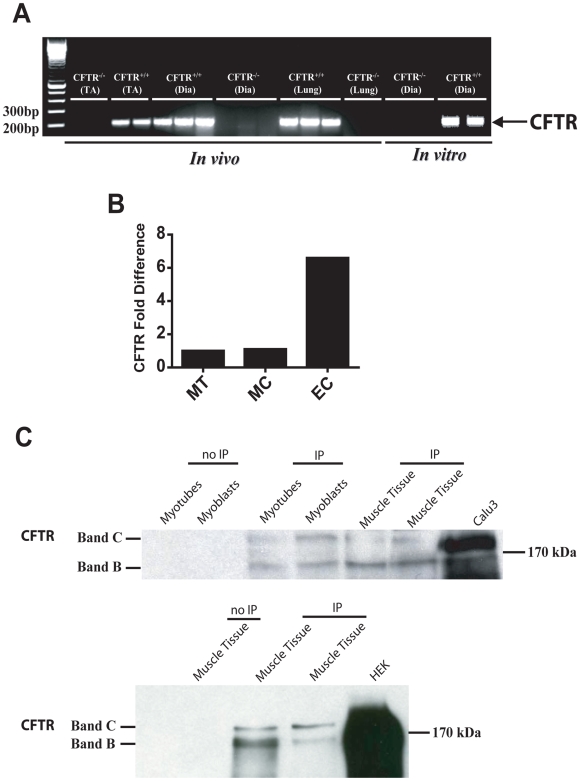
Figure 1. Expression of CFTR in normal skeletal muscle.
(A) CFTR transcripts in lung, tibialis anterior (TA), and diaphragm (Dia) muscle tissue (in vivo) as well as in cultured myotubes from wild-type (Cftr+/+) mouse diaphragms (in vitro). (B) Relative quantification of human CFTR mRNA in skeletal muscle tissue (MT), cultured E6/E7 skeletal muscle cells (MC), and cultured epithelial cells (EC) from human nasal mucosa. (C) Western blotting for human CFTR after immunoprecipitation (IP) of CFTR protein in human skeletal muscle tissue and cultured human muscle cells (myotubes and myoblasts), as well as CFTR-overexpressing positive control cells (Calu3 or HEK). Note the presence of both mature (Band C) and immature (Band B) forms of CFTR. Top Panel: lysate amounts for IP were 1000 (lanes 3–5), 2000 (lane 6), and 200 µg (lane 7). Bottom Panel: lysate amounts for IP were 3000, 1500, and 1000 µg for lanes 2–4, respectively.