FIGURE 6.
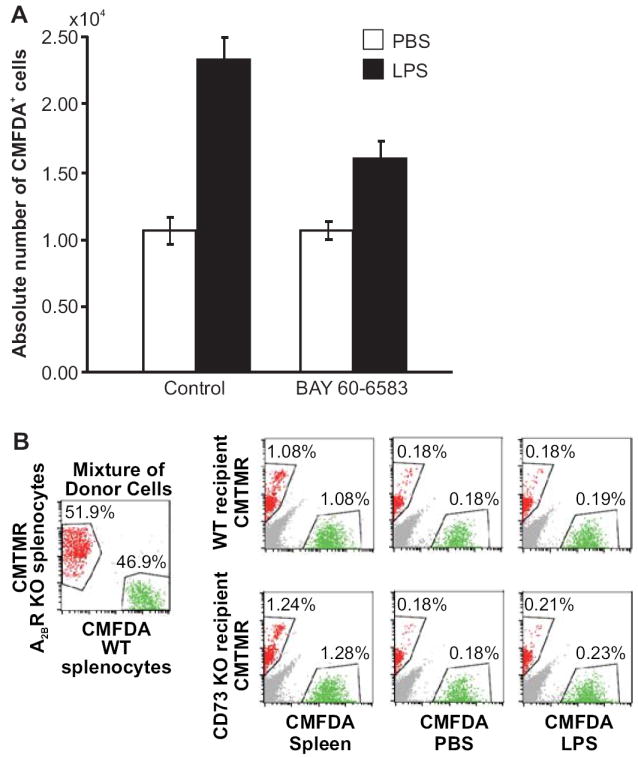
The A2B adenosine receptor agonist, BAY 60-6583, inhibits the increased lymphocyte migration into draining lymph nodes of CD73-deficient mice. A. LPS (1 μg) was injected into the left front footpad of cd73+/+ and cd73-/- mice and an equivalent volume of PBS was injected into the right front footpad. Twenty-two h and 30 min after the LPS injection, the mice were injected i.v. with BAY 60-6583 (320 μg/kg) or an equivalent volume of diluted PEG 400 carrier and 30 min later with 107 CMFDA-labeled cd73+/+ splenocytes. One h after the injection of labeled splenocytes, lymph nodes were harvested and the total numbers of cells in each lymph node were counted and the percentages of CMFDA+ cells were determined by flow cytometry (n=20-26, p=0.0034 for diluted PEG 400 vs. BAY 60-6583 in draining lymph nodes, data combined from 4 separate experiments). B. LPS (1 μg) was injected into the left front footpad of wild type and cd73-/- mice and an equivalent volume of PBS was injected into the right front footpad (5 mice/group). Twenty-three h later, the mice were injected i.v. with an equal mixture of 107 wild type and A2BR-/- splenocytes labeled with CMFDA or CMTMR, respectively. One h later, brachial lymph nodes were harvested and the percentages of CMFDA+ and CMTMR+ lymphocytes were determined by flow cytometry. Data are representative of 1 out of 2 experiments.
