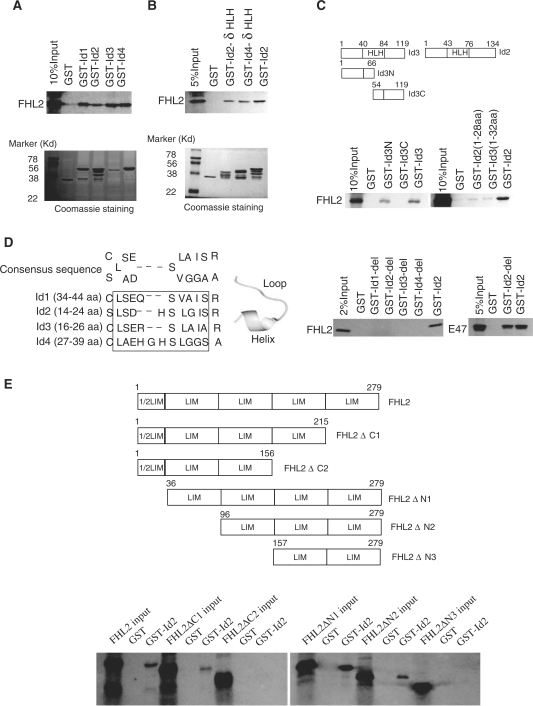
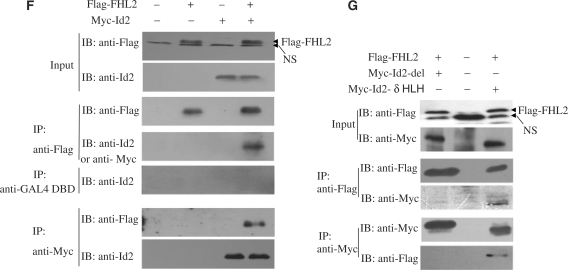
Figure 2.
FHL2 interacts with Id proteins in vitro and in vivo. (A) GST-pulldown assays were performed with in vitro-translated, [35S]-labeled FHL2 in the presence of GST–Id (Id1–4) fusion proteins. GST protein was used as a control. (B) GST-pulldown assays were performed with [35S]-labeled FHL2 and GST alone, GST–Id2–δHLH, GST–Id4–δHLH or GST–Id2. (C) The top panel is the schematic illustration of Id3 and its mutants. GST alone, GST–Id3-N, GST–Id2-C and GST–Id2 were used to pull down the full-length FHL2 (bottom panel). (D) The left panel shows the alignment of the relatively conserved region within the N termini of Id proteins (Id1–4). The sequence in the pane was deleted in Id-del mutants. The middle panel shows the representative loop–helix structure of these conserved amino acids. GST alone, GST–Id-del mutants or GST–Id2 were used to pull down the full-length FHL2 or E47 (right panel). (E) The upper panel is the schematic illustration of FHL2 and its mutants. GST-pulldown assays were performed with various IVT–FHL2 mutants and GST–Id2 or GST alone. (F) COS-7 cells were transfected with Flag-FHL2, Myc-Id2 or their combination. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated and immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. (G) COS-7 cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids. After 48 h transfection, cells were lysed and underwent CoIP experiments using the indicated antibodies. NsIgG, non-specific IgG. NS, non-specific band.